A model that attracted quite a bit of interest in macroeconomics in the 1970s was the St. Louis model. The underlying idea was to calculate fiscal and monetary impact and long run cumulative dynamic multipliers, by relating output (growth)to government expenditure (growth)and money supply (growth). The assumption was that both government expenditures and the money supply were exogenous. Estimation of a St. Louis type model using quarterly data from 1960:I-1995:IV results in the following output (HAC standard errors in parenthesis): 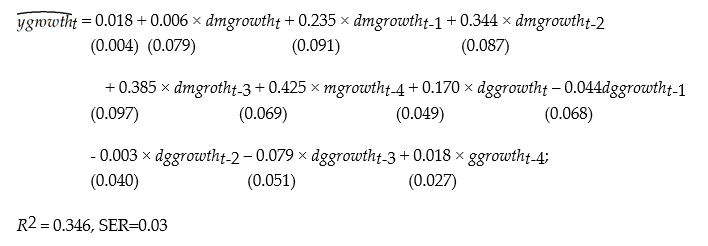
where ygrowth is quarterly growth of real GDP, mgrowth is quarterly growth of real money supply (M2), and ggrowth is quarterly growth of real government expenditures. "d" in front of ggrowth and mgrowth indicates a change in the variable.
(a)Assuming that money and government expenditures are exogenous, what do the coefficients represent? Calculate the h-period cumulative dynamic multipliers from these. How can you test for the statistical significance of the cumulative dynamic multipliers and the long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier?
(b)Sketch the estimated dynamic and cumulative dynamic fiscal and monetary multipliers.
(c)For these coefficients to represent dynamic multipliers, the money supply and government expenditures must be exogenous variables. Explain why this is unlikely to be the case. As a result, what importance should you attach to the above results?
Definitions:
Check Register
A record of all transactions in a checking account, including checks written, deposits made, fees paid, ATM withdrawals, and so on.
Bank Statement
A statement that includes all transactions that have occurred for a period of approximately one month.
Discrepancies
Differences or inconsistencies found within related facts, figures, or statements, often requiring further investigation or adjustment.
Variable N
A symbol or placeholder for an unknown or changing quantity in mathematics and science.
Q3: Assume that data are available on other
Q7: If the instruments are not exogenous,<br>A)you cannot
Q9: You learned in intermediate macroeconomics that
Q11: (Requires Calculus)For the case of the multiple
Q17: The binary variable interaction regression<br>A)can only be
Q37: (Requires Appendix material)State and prove the Cauchy-Schwarz
Q42: In Macroland,planned aggregate expenditure equals 100,000 +
Q43: (Requires Appendix material)Briefly describe the difference between
Q59: The textbook shows that ln(x +
Q69: The money supply in Econland is 1,000,and