(Requires Appendix material)Your textbook states that in "the distributed lag regression model, the error term ut can be correlated with its lagged values. This autocorrelation arises, because, in time series data, the omitted factors that comprise ut can themselves be serially correlated."
(a)Give an example what the authors have in mind.
(b)Consider the ADL model, where the X's are strictly exogenous, and there is no autocorrelation (and/or heteroskedasticity)in the error term. 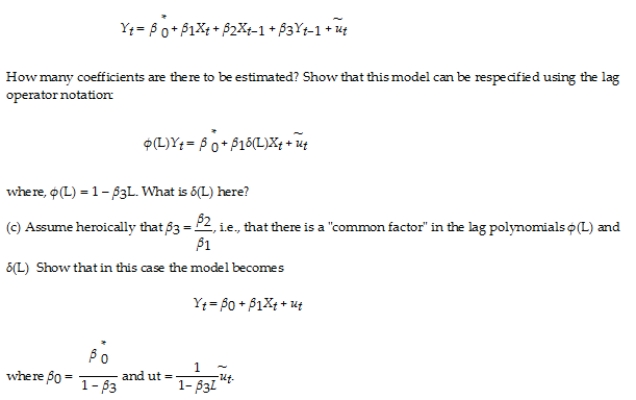 (d)Explain why autocorrelation in this model can be seen as a "simplification," not a "nuisance." Can you use the F-test to test the above hypothesis? Why or why not?
(d)Explain why autocorrelation in this model can be seen as a "simplification," not a "nuisance." Can you use the F-test to test the above hypothesis? Why or why not?
Definitions:
Human Genome
The complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoding for the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of human beings.
Similar Gene
A gene that shares sequence similarity or functional similarities with another gene, often within the same organism or across different species.
RNA Interference
A process in biology where RNA molecules prevent gene expression or translation through the neutralization of targeted mRNA molecules.
Transcription Factors
Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate the transcription of genetic information from DNA to mRNA.
Q7: In the basic Keynesian model,a decrease in
Q10: A joint hypothesis that is linear
Q14: The Times Series Regression with Multiple Predictors<br>A)is
Q20: Departures from stationarity<br>A)jeopardize forecasts and inference based
Q33: You have estimated the relationship between
Q36: The major distinction between the experiments and
Q45: If the estimates of the coefficients of
Q62: The M2 measure of money consists of
Q62: Assume that you have collected cross-sectional
Q97: The profit gained by the Bank of