A model that attracted quite a bit of interest in macroeconomics in the 1970s was the St. Louis model. The underlying idea was to calculate fiscal and monetary impact and long run cumulative dynamic multipliers, by relating output (growth)to government expenditure (growth)and money supply (growth). The assumption was that both government expenditures and the money supply were exogenous. Estimation of a St. Louis type model using quarterly data from 1960:I-1995:IV results in the following output (HAC standard errors in parenthesis): 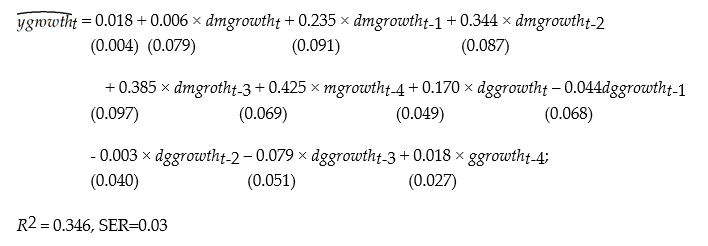
where ygrowth is quarterly growth of real GDP, mgrowth is quarterly growth of real money supply (M2), and ggrowth is quarterly growth of real government expenditures. "d" in front of ggrowth and mgrowth indicates a change in the variable.
(a)Assuming that money and government expenditures are exogenous, what do the coefficients represent? Calculate the h-period cumulative dynamic multipliers from these. How can you test for the statistical significance of the cumulative dynamic multipliers and the long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier?
(b)Sketch the estimated dynamic and cumulative dynamic fiscal and monetary multipliers.
(c)For these coefficients to represent dynamic multipliers, the money supply and government expenditures must be exogenous variables. Explain why this is unlikely to be the case. As a result, what importance should you attach to the above results?
Definitions:
WACC
Weighted Average Cost of Capital, a calculation of a firm's cost of capital in which each category of capital is proportionately weighted.
Capital Budgeting
The process of evaluating and selecting long-term investments that are consistent with the firm's goal of wealth maximization.
After-Tax Cost
The net cost of a transaction or investment after the effects of taxes are considered, often used in analyzing the cost of financing options.
Specific Capital
This refers to the various types of capital (debt, equity, etc.) a company uses for financing its operations and investments, with each type having its own cost and characteristics.
Q8: In the case of the simple regression
Q18: Holding money as a store of wealth
Q30: When money is the basic measure of
Q42: To convey information about the dynamic multipliers
Q47: The two conditions for instrument validity are
Q97: The profit gained by the Bank of
Q122: Induced planned aggregate expenditure is the portion
Q135: Changes in government purchases affect planned aggregate
Q172: Consumption,planned private-sector investment,government purchases,and net exports are
Q196: In the basic Keynesian model,a $1 billion