On December 31,20X2,the Esther Company purchased 80% of the outstanding common shares of the Jane Company for $7.5 million in cash.On that date,the shareholders' equity of Jane totalled $6 million and consisted of $1 million in no par common shares and $5 million in retained earnings.Both companies use the straight-line method to calculate depreciation and amortization.Goodwill,if any arises as a result of this business combination,is written down if there is a permanent impairment in its value.
For the year ending December 31,20X4,the statements of comprehensive income for Esther and Jane 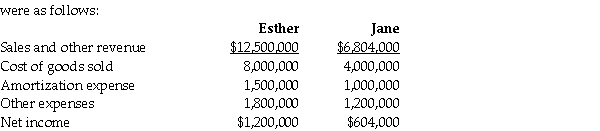
At December 31,20X4,the condensed statement of financial position for the two companies were as follows: 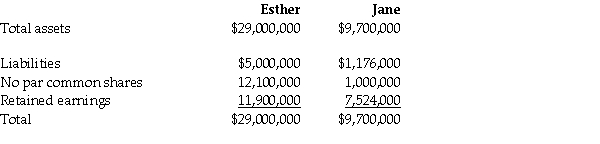
OTHER INFORMATION:
1.On December 31,20X2,Jane had a building with a fair value that was $450,000 greater than its carrying value.The building had an estimated remaining useful life of 15 years.
2.On December 31,20X2,Jane had inventory with a fair value that was $150,000 less than its carrying value.This inventory was sold in 20X3.
3.During 20X3,Jane sold merchandise to Esther for $100,000,a price that included a gross profit of $50,000.During 20X3,40% of this merchandise was resold by Esther and the other 60% remained in its December 31,20X3 inventories.On December 31,20X4,the inventories of Esther contained merchandise purchased from Jane on which Jane had recognized a gross profit in the amount of $20,000.Total sales from Jane to Esther were $150,000 during 20X4.
4.During 20X4,Esther declared and paid dividends of $300,000 while Jane declared and paid dividends of $100,000.
5.Esther accounts for its investment in Jane using the cost method.
Required:
Calculate goodwill on the consolidated balance sheet at December 31,20X4 under the entity method and the parent-company extension method.Explain the differences between the two balances.
Definitions:
World System
A viewpoint that emphasizes the global interconnections and dependencies of economies and cultures.
Peripheral Countries
Countries often characterized by their marginal position within the global economic system, typically having less developed economies and depending on core countries for capital.
Raw Materials
The basic material from which a product is made, typically referring to natural resources that are used in production.
GDP
Gross Domestic Product, a monetary measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a period by a country.
Q1: What is often the main motivation behind
Q7: On September 1,20X5,High Limited decided to buy
Q10: When the International Accounting Standards Board amends
Q17: There is certain information that reportable segments
Q33: Describe the major differences that exist in
Q35: Blue Sky Inc.(BSI)is a public company which
Q49: is the marketing term for people,whether they
Q96: Which of the following describes the term
Q261: target market refers to<br>A) people who could
Q262: Publix Supermarkets and The Little Clinic signed