A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of 6.0 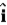
M/s and moves in the xy plane with a constant acceleration of (−2.0 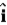
+ 4) 0 
) m/s2.At the instant the particle achieves its maximum positive x coordinate,how far is it from the origin?
Definitions:
Contribution Margin
The difference between sales revenue and variable costs, indicating how much contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profits.
Direct Manufacturing Cost
Costs that are directly attributable to the production of a specific product, including direct materials and direct labor.
Indirect Manufacturing Cost
Costs related to production that are not directly associated with the product, such as maintenance, supervision, and utilities.
Incremental Manufacturing Cost
The additional cost incurred to produce one more unit of a product, often considered for decision-making in production processes.
Q13: The area under a graph of a<sub>x</sub>
Q18: Planets go around the sun in elliptical
Q45: Net present value (NPV) assumes that intermediate
Q52: A pendulum bob has potential energy U<sub>0</sub>
Q55: A student is sitting on the right
Q57: A 3.0-kg mass sliding on a frictionless
Q69: An astronaut who weighs 800 N on
Q71: Identical masses m are attached to identical
Q77: _ projects do not compete with each
Q88: A 1.0-kg ball is attached to the