To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank, 90 individuals were randomly selected, and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual; 1 for males, and 0 for females.
Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Train + β4Gender + ε 
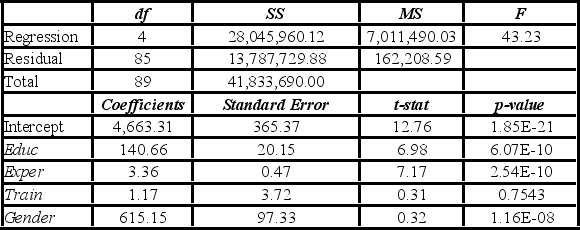 Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε 
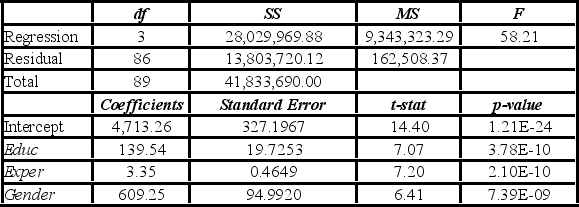 The variable Train is deleted from Model A which results in Model B. Which of the following justifies this choice?
The variable Train is deleted from Model A which results in Model B. Which of the following justifies this choice?
Definitions:
Attitudes
psychological tendencies expressed by evaluating entities with some degree of favor or disfavor.
Values
Fundamental beliefs or standards of behavior that guide decisions and actions.
Beliefs
are convictions or acceptances that something exists or is true, especially without proof.
Decision Process
The sequence of cognitive steps taken by individuals or groups in selecting among alternatives to make a decision.
Q9: _ patterns are caused by the presence
Q48: Investment institutions usually have funds with different
Q63: One of the key differences between an
Q68: An option seller can avoid a loss
Q71: An economist estimates the following model: y
Q75: Consider the following information regarding a response
Q76: The log-log regression model is _ in
Q96: Which of the following is not true
Q106: Donna Warne purchased a share of company
Q112: The moving average method is one of