To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank, 90 individuals were randomly selected, and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual; 1 for males, and 0 for females.
Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Train + β4Gender + ε 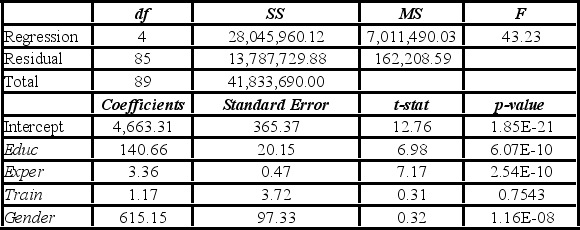 Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε 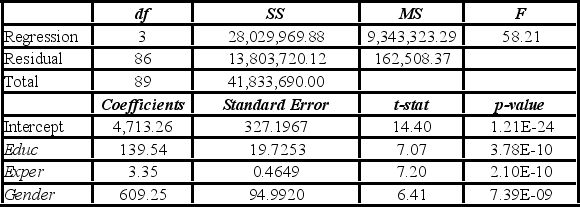 A group of female managers considers a discrimination lawsuit if on average their salaries can be statistically proven to be lower by more than $500 than the salaries of their male peers with the same level of education and experience. Using Model B, what is the alternative hypothesis for testing the lawsuit condition?
A group of female managers considers a discrimination lawsuit if on average their salaries can be statistically proven to be lower by more than $500 than the salaries of their male peers with the same level of education and experience. Using Model B, what is the alternative hypothesis for testing the lawsuit condition?
Definitions:
Ethical Issues
Concerns or dilemmas that involve right or wrong behavior in the business realm.
Institute For Supply Management
A professional organization that provides education, research, and certification for supply management and procurement professionals.
Few Suppliers
Refers to a supply chain strategy where a company relies on a limited number of suppliers for its raw materials or components, aiming to build closer, more collaborative relationships and ensure better quality control.
Vertical Integration
A strategy where a company expands its business operations into different steps on the same production path, such as when a manufacturer owns its supplier and/or distributor.
Q28: Consider the following sample regression equation <img
Q35: To examine the differences between salaries of
Q39: The following data show the demand for
Q40: Quarterly sales of a department store for
Q48: A bank manager is interested in assigning
Q57: An over-the-counter drug manufacturer wants to examine
Q91: The following table shows the annual revenues
Q108: A researcher wants to understand how an
Q112: The following scatterplot shows productivity and number
Q117: SHY (NYSEARCA: SHY) is a 1−3-year Treasury