The mean free path of an oxygen molecule is 2.0 × 10-5 m,when the gas is at a pressure of 120 Pa and a temperature of 275 K.The atomic mass of oxygen is 16.0 g/mol,the Boltzmann constant is 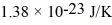 ,Avogadro's number is
,Avogadro's number is 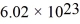 molecules/mole,and the ideal gas constant is
molecules/mole,and the ideal gas constant is 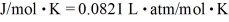 .The radius of an oxygen molecule is closest to
.The radius of an oxygen molecule is closest to
Definitions:
Coefficient of Determination
This indicates the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that can be explained by the independent variable(s) in a regression model, quantifying the predictive power of the model.
Units
Basic quantities or measurements used to express and compare physical quantities.
Sample Size
Refers to the number of observations or data points collected in a study or used in statistical analysis.
Symbols
Characters or marks that are used to represent objects, quantities, or relations in mathematical expressions, equations, or in general notation.
Q5: Find the speed of an ocean wave
Q9: A 10.0-kg uniform ladder that is 2.50
Q16: While spinning down from 500.0 rpm to
Q32: A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.80
Q39: For the circuit shown in the figure,determine
Q40: Two very large,flat plates are parallel to
Q44: The emf and the internal resistance of
Q45: A 12,000-N car is raised using a
Q45: How much work is done by 3.00
Q47: In the circuit shown in the figure,all