On September 1, 20X5, Frank Limited decided to buy 70% of the shares outstanding of Jake Inc. for $840,000. Frank paid for this acquisition by using cash of $500,000 and marketable securities for the remaining amount. The balances showing on the statement of financial position for the two companies at August 31, 20X5, are as follows:  After a review of the financial assets and liabilities, Frank determines that some of the assets of Jake have fair values different from their carrying values. These items are listed below:
After a review of the financial assets and liabilities, Frank determines that some of the assets of Jake have fair values different from their carrying values. These items are listed below:
• Inventory has a fair value of $130,000.
• The building has a fair value of $1,090,000. The remaining useful life of the building is 20 years.
• A customer list has a fair value of $200,000. The trademark is estimated to have a useful life of 10 years.
• The bonds payable have a fair value of $720,000 and are due on August 31, 20X9.
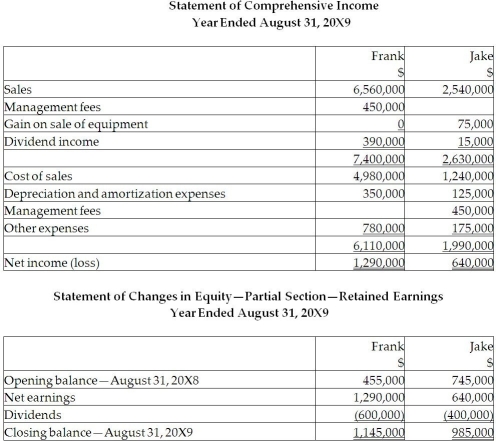
During the 20X9 fiscal year, the following events occurred:
1. Frank sold merchandise to jake for . Profit margin on these sales . Jake still has Inventory on hand of . Included in the opening inventory of Jake for is merchandise purchased from Frank in for . The gross profit mar gin on these sales was
2. Jake sold merchandise to Frank for . The gross margin on these sales was . At the end of the year, of this was still in Frank's inventory. Included in the opening inventory of Frank for was merchandise purchased from Jake in for . The profit margin on these sales was .
3. During , Jake sold to Frank equipment resulting in a gain to Jake of . At the time, the original cost and accumulated depreciation to date for the equipment on the Jake's books were and 160,000 . The remaining useful life for this equipment is 15 years. Depreciation is fully recorded in the year of purchase and no depreciation is recorded in the year of disposal by both companies.
4. During , Jake paid management fees of to Frank.
5. During 20X9, lake paid dividends of and Frank paid dividends of . 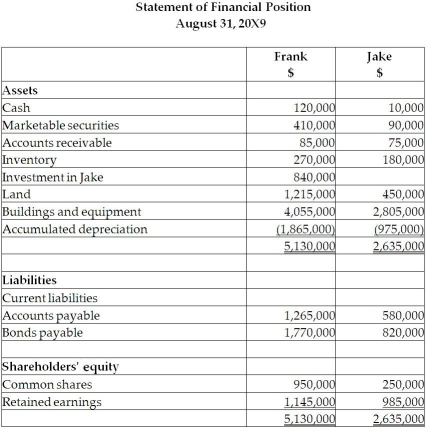
 Required:
Required:
Calculate the balance in the investment in Jake account at August 31, 20X9, if the company accounted for this subsidiary using the equity basis.
Calculate the balance in the investment in Jake account at August 31, 20X9, if the company accounted for Jake as an associate using the proprietary theory basis for the equity method.
Explain the difference between the two balances.
Goodwill is determined using the parent-company extension approach.
Definitions:
Truth
The state or quality of being in accordance with fact or reality, often considered as an objective concept in philosophy.
Harm
Physical injury or damage caused to something or someone, often a result of accidents, negligence, or intentional actions.
Questionnaire
A research instrument consisting of a series of questions and other prompts for the purpose of gathering information from respondents.
Scientific Method
A systematic and logical approach to discovering how things in the universe work, involving observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and conclusion.
Q1: On December 31, 20X5, Space Co.
Q10: There are a number of possible approaches
Q11: The accounting equation may be expressed as
Q21: Under IFRS 8, certain reconciliations, such as
Q54: Liabilities represent an "inside" interest in a
Q64: Refer to the table above. What will
Q66: An increase in a revenue account may
Q67: On what should the decision to invest
Q71: The accounting equation shows the relationship among
Q72: Refer to the table above. Calculate the