Telecom Company produces a cell phone that sells for $150,and a smart phone that sells for $350.Last year,total overhead costs of $550,000 were allocated based on direct labor hours.A total of 12,000 direct labor hours were required last year to build 6,000 cell phones (2 hours per unit),and 10,000 direct labor hours were required to build 2,000 smart phones (5 hours per unit).Total direct labor and direct materials costs for last year were:
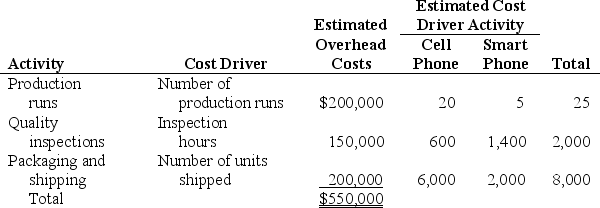
Management of Telecom Company would like to use activity-based costing to allocate overhead rather than using one plantwide rate based on direct labor hours.The following estimates are for the activities and related cost drivers identified as having the greatest impact on overhead costs.
(1) Calculate the direct materials cost per unit and direct labor cost per unit for each product.
(2) a. Using the plantwide allocation method, calculate the predetermined overhead rate and determine the overhead cost per unit for the cell phone and smart phone products.
b. What is the product cost per unit for the cell phone and smart phone products?
(3) a. Using the activity-based costing allocation method, calculate the predetermined overhead rate for each activity.
b. Using the activity-based costing allocation method, allocate overhead to each product. Determine the overhead cost per unit
c. What is the product cost per unit for the cell phone and smart phone products?
(4) Calculate the per unit profit for each product using the plantwide approach and the activity-based costing approach. Comment on the difference in the results between the two approaches
Definitions:
Machine-Hours
A measure of the amount of time machines are used in the production process, often used for allocating manufacturing overhead.
Batches
Quantities of material or products processed or produced at the same time in a manufacturing process.
Product Margins
refer to the difference between the selling price of a product and its production costs, indicating the profitability of the product.
Activity-Based Costing
A costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity with resources to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each.
Q10: Nonmanufacturing costs consist of selling costs and
Q16: Refer to Exhibit 3-2.What is the overhead
Q16: Refer to Exhibit 8-2.Calculate the net present
Q22: The appropriate rate to be used for
Q28: Soda Manufacturing Company provides vending machines for
Q31: Which of the following would be a
Q38: All of the following are reasons that
Q45: The Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)provides formal
Q63: Flannery Inc.produces identical tables in large batches.Which
Q98: What is the transfer price per compressor