The below table shows the average utility (in utils) obtained from the consumption of goods A and B.Table 7.3
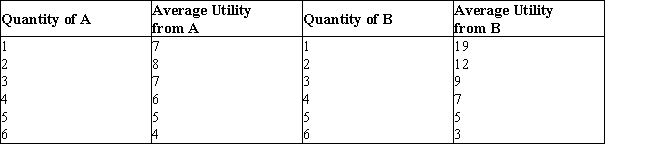
-Assume MUX = 30 utils, MUY = 15 utils, PX = $2, and PY = $0.50. This consumer:
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The cost at which the amount of a product sought by consumers matches the amount available from suppliers, leading to equilibrium in the market.
Demand Curve
A graph showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of that good consumers are willing and able to purchase, typically depicting a downward slope.
Competitive Market
A market structure characterized by numerous buyers and sellers, ensuring no single participant has the power to significantly influence prices.
Average Total Cost
The per unit cost of production, calculated by dividing the total cost of production by the quantity of output produced.
Q5: Price elasticity of demand is the sole
Q9: In Figure 10.3, at equilibrium, the firm
Q38: Sellers are more willing to supply a
Q44: Refer to Table 9.2. If we assume
Q50: In the long run, a perfectly competitive
Q52: If an increase in the price of
Q81: Refer to Table 7.4. What is the
Q94: Other things remaining the same, if a
Q103: Ceteris paribus, a 10 percent increase in
Q104: Some competitive firms are willing to operate