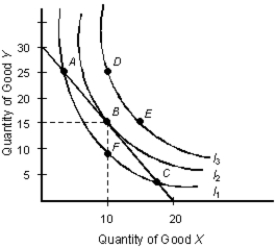
The below figure shows the various combinations of the goods X and Y that yield different levels of utility.Figure 7.3
-With expansion in the level of output, total fixed cost:
Definitions:
Utility Theory
A framework in economics and finance that describes how individuals make choices based on the perceived benefit or satisfaction they will gain, aiming to maximize utility.
Economists
Professionals who study how societies use resources to produce goods and services and distribute them among individuals.
Loss Aversion
The strong tendency to regard losses as considerably more important than gains of comparable magnitude—and, with this, a tendency to take steps (including risky steps) to avoid possible loss.
Affective Forecasting
Predicting one’s own emotional response to upcoming events.
Q3: As long as there are fixed resources,
Q6: Identify the international organization that makes loans
Q8: When the marginal-cost curve lies above the
Q38: To practice price discrimination, a firm:<br>A)must face
Q66: The substitution effect occurs because when the
Q68: Airlines can increase profits by charging higher
Q82: Arc elasticity is calculated as _.<br>A) <img
Q87: In the short run when output is
Q93: Refer to Figure 9.3. If the firm
Q98: A firm's total revenue is $400 for