The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.2
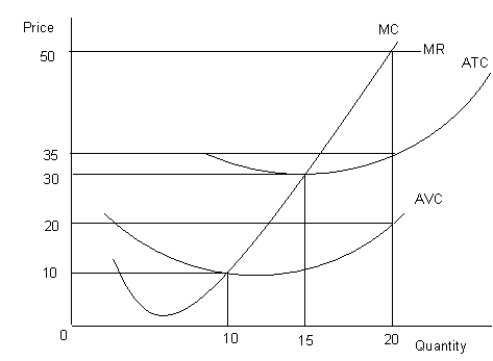 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-Refer to Figure 10.2. What is the firm's total fixed cost at the profit-maximizing output level?
Definitions:
Opportunity Cost
Abstaining from possible rewards offered by other selections upon choosing one.
Agricultural Output
The total production of crops, livestock, and other agricultural goods within a specific period, usually expressed in quantity or value terms.
Rural India
Refers to the countryside areas of India, often characterized by agricultural communities, lesser-developed infrastructure, and traditional lifestyles.
Opportunity Cost
The value of the next best alternative that must be foregone as a result of making a decision.
Q2: If the marginal utility of a product
Q7: The existence of externalities in a market
Q16: At the twenty-fifth anniversary of the Woodstock
Q31: An increase in income _.<br>A)makes the budget
Q82: Asymmetric information arises when:<br>A)both the parties to
Q88: Why does a network externality arise?<br>A)Each additional
Q117: "Throwing good money after bad" is also
Q118: Consider the monopolist described in the Figure
Q130: Given the above equation, the quantity of
Q131: Under perfect competition, the average revenue curve