The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.5
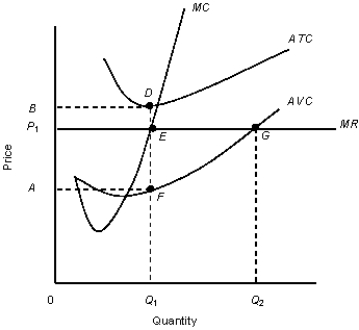 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve.ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-For a perfectly competitive firm, in the short run, which of the following statements is true?
Definitions:
NPVGO
Net Present Value of Growth Opportunities; the present value of future investments' cash flows minus initial investments.
Dividend Growth Rate
The annual percentage rate of growth of a company’s dividend payments to shareholders.
Investor's Return
The positive or negative shift in an investment's financial value during a set interval, portrayed as a percentage of the investment's initial price.
Stock Price
The cost of purchasing a share of a company's stock, determined by the supply and demand for it in the market.
Q3: If significant barriers to entry exist in
Q44: If the demand for liquor is elastic
Q52: In the United States, monopoly regulation began
Q55: Which of the following is a measure
Q76: For a perfectly competitive firm the break-even
Q79: The cost borne by an individual user
Q85: Education is a good example of a
Q88: A monopolist enjoys the least market power
Q88: Marginal utility is total utility divided by
Q106: The theory of bounded rationality states that