The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
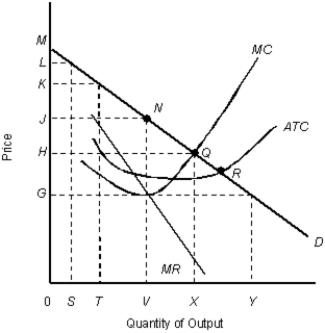 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-If a monopolist's demand curve shifts to the left such that it becomes tangent to the ATC curve at the output for which marginal revenue equals marginal cost, the monopolist will make only a normal profit.
Definitions:
Neurons
Specialized neurons in the nervous system that communicate information via electrical and chemical signals.
Summation
The process of adding together excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs).
Temporal
Relating to time or denoting time as opposed to space.
Spatial Summation
A mechanism in neural communication where multiple presynaptic neurons together stimulate a postsynaptic neuron to threshold, causing it to fire an action potential.
Q11: In which market structure model(s) is product
Q14: According to Figure 14.2, if the marginal
Q40: Which of the following statements contradicts an
Q49: If a monopolist is producing at the
Q50: Refer to Table 11.4 and calculate the
Q58: If all firms in a monopolistically competitive
Q95: The free rider problem arises when a
Q106: In the short run, a firm continues
Q118: As the price of a good declines,
Q131: Under perfect competition, the average revenue curve