The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
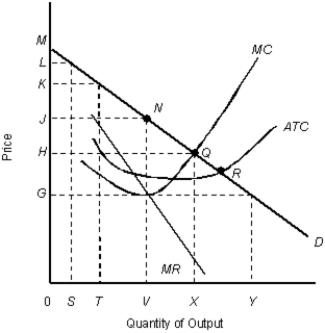 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-By discriminating between the consumers, the monopolist actually takes away a portion of the consumer surplus.
Definitions:
Cooperative Outcome
A result in decision-making where all parties work together to achieve a mutually beneficial solution, often in contrast to competitive or adversarial outcomes.
Oil Companies
Corporations that extract, produce, refine, or market oil and its derivative products.
Air Travel
The act of moving from one place to another through the atmosphere, typically in an airplane.
Profit-maximizing Price
The price level at which a business can achieve the highest possible profit, balancing costs with sales volume.
Q17: A firm that was initially a monopsonist,
Q39: Under perfect competition, existing firms leave the
Q60: In general, the number of firms is
Q65: According to the per se rule, activities
Q70: Refer to Figure 11.2. In order to
Q70: Under the second phase of antitrust policy
Q81: The price of a resource declines when:<br>A)both
Q102: Why does an efficiency loss arise under
Q107: Refer to Figure 12.4. What is the
Q119: If the price of the output produced