The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
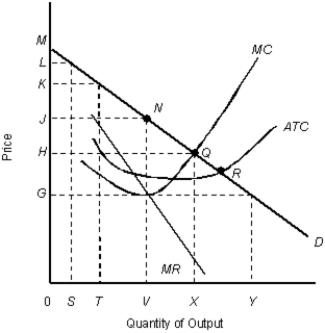 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-A monopolist produces at the minimum point of the average total cost curve in the long run.
Definitions:
Myelin Sheath
A protective covering made of fatty substances and proteins that surrounds the axons of many neurons, enhancing the speed of nerve impulse transmission.
Neuron Structure
Describes the anatomy of a neuron, including parts such as the cell body, dendrites, axon, and synaptic terminals, which facilitate nerve impulse transmission.
Electrical Cord
A flexible cable comprised of one or more electrical conductors, typically encased in insulation, used to transmit power.
Nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath of nerve fibers where axonal membranes are exposed, enabling rapid transmission of nerve impulses.
Q20: When studying the market for resources, it
Q29: The characteristic that distinguishes a monopolistically competitive
Q29: Refer to Figure 10.3 and identify the
Q31: A monopolistically competitive market is marked by
Q48: As a perfectly competitive firm produces at
Q50: In the long run, a perfectly competitive
Q70: Refer to Figure 11.2. In order to
Q75: In the context of market structure, the
Q88: At long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive
Q99: The producer can raise the level of