Exhibit 10.1
The following questions are based on the problem description and the output below.
A college admissions officer wants to evaluate graduate school applicants based on their GMAT scores, verbal and quantitative. Students are classified as either successful or not-successful in their graduate studies. The officer has data on 20 current students, ten of whom are doing very well (Group 1) and ten who are not (Group 2) . 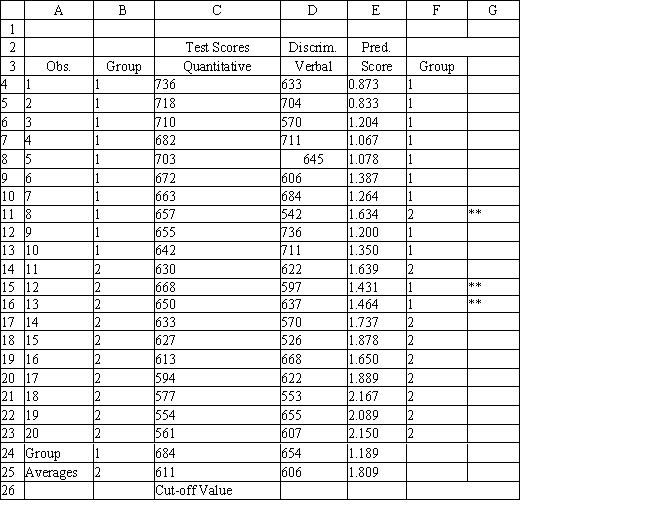
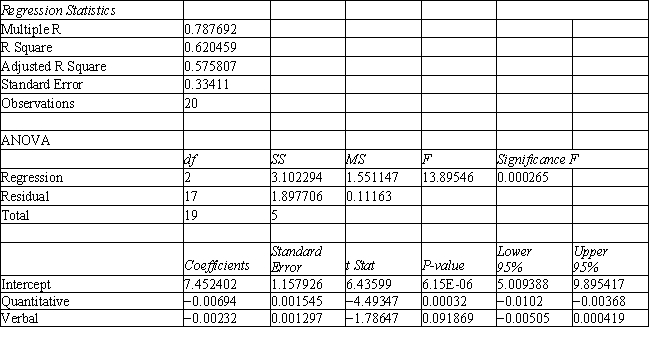

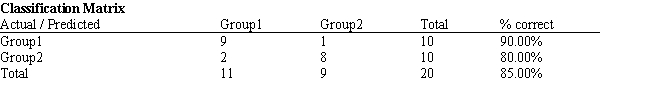

-Refer to Exhibit 10.1. Suppose that for a given observation, the difference between Mahalanobis distances between group 1 and 2 (G1-G2) is big and negative. This means that
Definitions:
Fixed-ratio Schedule
A reinforcement strategy in operant conditioning where a response is rewarded only after a specified number of correct responses.
Fixed-interval Schedule
A type of reinforcement schedule in operant conditioning where rewards are delivered at fixed intervals of time, as long as the correct response is made.
Secondary Reinforcers
Conditioned stimuli that acquire reinforcement value through their association with primary reinforcers.
Conditioned Reinforcers
Stimuli or rewards that have become reinforcing by being paired with another reinforcer, sometimes called secondary reinforcers.
Q1: A company needs to ship 100
Q15: A barber shop has one barber,a Poisson
Q33: Refer to Exhibit 7.1.What formula goes in
Q35: Refer to Exhibit 9.1.Interpret the meaning of
Q44: Decision models are applicable when<br>A)there are multiple
Q47: Solve the following minimal spanning tree problem
Q58: The term "stationary data" means that<br>A)the mean
Q70: Refer to Exhibit 11.2.What is the 2-month
Q74: A company wants to build a new
Q75: Refer to Exhibit 11.7.What are predicted sales