Cindy Ho,VP of Finance at Discrete Components,Inc = 001,the Appropriate Decision Is _________
Cindy Ho,VP of Finance at Discrete Components,Inc.(DCI) ,theorizes that the discount level offered to credit customers affects the average collection period on credit sales. Accordingly,she has designed an experiment to test her theory using four sales discount rates (0%,2%,4%,and 6%) by randomly assigning five customers to each sales discount rate.An analysis of Cindy's data produced the following ANOVA table. 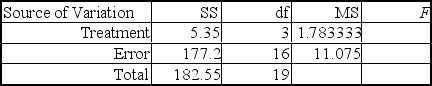
Using = 0.01,the appropriate decision is _________.
Definitions:
Marginal Revenue Product
The additional revenue generated from employing one more unit of a factor of production.
Marginal Product
The extra output that comes from increasing a particular input by one unit, while keeping all other inputs unchanged.
Marginal Revenue Product
The extra revenue generated by employing one more unit of a factor, such as labor or capital.
Marginal Revenue Product
The additional revenue generated from using one more unit of a resource.
Q30: Suppose you are testing the null hypothesis
Q34: An acceptable method of managing multicollinearity in
Q59: Which of the following iterative search procedures
Q67: Suppose a population has a mean of
Q73: Golf course designer Roberto Langabeer is
Q85: The high and low values of the
Q89: Suppose 90% of students in some specific
Q91: A multiple regression analysis produced the
Q92: From the following scatter plot,we can say
Q94: If x and y in a regression