One model for the spread of an epidemic is that the rate of spread is jointly proportional to the number of infected people and the number of uninfected people.In an isolated town of 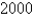 inhabitants,
inhabitants, 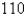 people have a disease at the beginning of the week and
people have a disease at the beginning of the week and 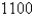 have it at the end of the week.How long does it take for
have it at the end of the week.How long does it take for 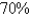 of the population to be infected?
of the population to be infected?
Definitions:
Parietal Lobe
A region of the brain located at the upper back area in the skull, responsible for processing sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Imprinting
The development of a social attachment to a stimulus experienced during a sensitive period of development.
Sensitive Periods
Times in an organism's development during which the organism is particularly receptive to certain stimuli, leading to lasting changes in behavior or capabilities.
Organism
A living individual, ranging from single-celled to complex multicellular entities, capable of performing biological functions.
Q1: Consider the polar equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6897/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q3: Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum
Q3: Find the center of mass of a
Q4: Find the center and the radius of
Q4: Find the volume common to two spheres,each
Q5: Use the guidelines of this section to
Q5: Approximate by a Taylor polynomial with degree
Q6: One model for the spread of an
Q18: The police are part of the system
Q23: The policing approach that concentrates on relatively