A man owns an Audi, a Ford, and a VW. He drives every day and never drives the same car two days in a row. These are the probabilities that he drives each of the other cars the next day:
Pr(Ford after Audi) = 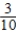 Pr(VW after Audi) =
Pr(VW after Audi) = 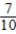 Pr(Audi after Ford) =
Pr(Audi after Ford) = 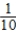 Pr(VW after Ford) =
Pr(VW after Ford) = 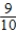 Pr(Audi after VW) =
Pr(Audi after VW) =  Pr(Ford after VW) =
Pr(Ford after VW) = 
What is the steady-state vector for this problem?
Definitions:
Neck
The neck is the part of the body that connects the head to the torso, containing structures that support movement, blood flow, and nerve communication.
Hypoglossal Nerves
Cranial nerves responsible for controlling the movements of most of the muscles in the tongue, crucial for speech, swallowing, and food manipulation.
Vagus Nerves
The tenth cranial nerves, extending from the brainstem to the abdomen, which play critical roles in controlling heart, digestive, and respiratory functions.
Sympathetic Division
A part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for physical activity by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising blood pressure.
Q11: The following tables give the rank and
Q20: Suppose the probability that a marksman will
Q42: State whether the problem relates to an
Q61: What does 050 represent in the following
Q74: If 11 people are qualified for the
Q107: A small town has 8000 adult males
Q112: From a deck of 52 ordinary playing
Q155: Substitute the given values of x, y,
Q160: Find the derivative of the given function.
Q173: A ball is drawn from a bag