Scenario I
Scenario I is based on and provides fabricated data consistent with the following study:
Barber, S. J., Rajaram, S., & Fox, E. B. (2012) . Learning and remembering with others: The key role of retrieval in shaping group recall and collective memory. Social Cognition, 30(1) , 121-132. doi:10.1521/soco.2012.30.1.121
In a typical experiment on collaborative memory, participants first encode information individually and later attempt to recall the information either individually or in a small group (collaboratively) . While the recall of the collaborative group is better than that of any individual, the summed recall of individuals typically is better than the recall of the collaborative group, a phenomenon termed collaborative inhibition. Barber, Rajaram, and Fox (2012) investigated this phenomenon during both the encoding and retrieval stages of memory.
Participants created sentences out of a word bank, which provided for the opportunity to encode this information. After completing this task, participants engaged in an unrelated task-solving mazes-for 10 minutes. Then, in a surprise memory test, they were asked to recall as many words from the word bank as possible (retrieval) .
Participants were randomly assigned to one of four groups. In the first group (Alone-Alone) , participants were studied individually during both the encoding and retrieval phases of the experiment. In the second group (Alone-Collaborative) , participants were studied individually during the encoding phase and studied as part of a three-member team (triad) during the retrieval phase. In the third group (Collaborative-Alone) , participants were studied in a triad during the encoding phase but individually during the retrieval phase. Finally, in the fourth group (Collaborative-Collaborative) , participants completed both phases of the experiment as part of a triad.
Fabricated results illustrating the major finding of Barber et al. (2012) are presented in Figure 6.1. This figure shows the percentage of words from the word bank accurately recalled as a function of group. For the two groups that experienced the retrieval phase individually, scores represent the summed retrieval of the individuals comprising the group. For the two groups that experienced the retrieval phase as part of a triad, scores simply represent the collaborative performance.
Figure 6.1 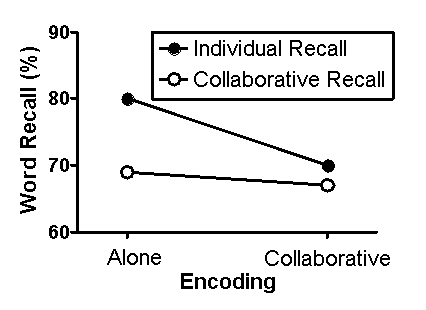
-(Scenario I) Which statement is true?
Definitions:
Parietal Lobes
Regions of the brain located behind the frontal lobes, involved in processing sensory information regarding the location of parts of the body as well as interpreting visual information and processing language and mathematics.
Spatial Location
The specific coordinates or position of an object or place in space.
Motor Control
The process by which humans and animals use their brain and muscular system to activate and coordinate the movements of their muscles and limbs.
Amygdala
A part of the brain's limbic system involved in emotion, decision-making, and memory processing.
Q5: Habituation occurs only in complex organisms.
Q8: (Scenario I) One possible explanation of collaborative
Q10: Which question pertains to psychological drug dependence?<br>A)Can
Q14: Krissy's _ becomes active when she tries
Q18: Kandel and colleagues stimulated the tail of
Q47: People usually do not report mind wandering
Q96: Eric has suffered damage to his hippocampus.
Q108: Retrieval of a memory may promote forgetting
Q160: In operant conditioning, presenting reinforcement upon the
Q191: Rescorla and Wagner theorized that a stimulus