Exhibit 17.9.A bank manager is interested in assigning a rating to the holders of credit cards issued by her bank.The rating is based on the probability of defaulting on credit cards and is as follows. 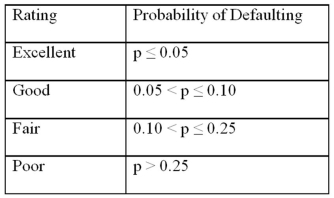 To estimate this probability,she decided to use the logistic model:
To estimate this probability,she decided to use the logistic model: 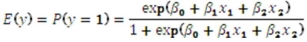 ,
,
where,
y = a binary response variable with value 1 corresponding to a default,and 0 to a no default,
x1 = the ratio of the credit card balance to the credit card limit (in percent),
x2 = the ratio of the total debt to the annual income (in percent).
Using Minitab on the sample data,she arrived at the following estimates: 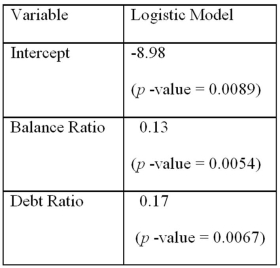 Note: The p-values of the corresponding tests are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The p-values of the corresponding tests are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Refer to Exhibit 17.9.Compute the predicted probability of defaulting for a person whose balance ratio is 5% and debt ratio is 30%.
Definitions:
Hypertension
A chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated, leading to health risks.
Minority
A group of people differentiated from the social majority based on ethnicity, race, religion, or other factors, often experiencing differential treatment or representation.
Inferiority
A feeling of being lesser in quality, value, or importance compared to others.
Hot and Cold Therapies
Treatment methods that involve the application of heat or cold to the body to reduce pain and promote healing.
Q3: Among the problems facing poor African American
Q10: Middle-class black women lawyers often attended black
Q14: Exhibit 13.1 The following is an incomplete
Q35: Exhibit 12-1 A card dealing machine deals
Q45: Exhibit 12.5 In the following table,individuals are
Q58: Exhibit 19-7.The following table shows the value
Q82: The R<sup>2</sup> of a multiple regression of
Q93: All criteria used for selecting the best
Q95: Exhibit 17.1.A researcher has developed the following
Q98: A regression equation was estimated as <img