Let 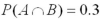 ,and
,and 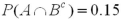 .Compute
.Compute 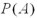 .
.
Definitions:
Type I Error
The incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis, also known as a "false positive" in statistical testing.
Measurement Error
Refers to the difference between the true value of a measurement and the recorded value due to various factors such as instrument error or human error.
T-tests
Statistical tests used to compare the means of two groups and determine if they are significantly different from each other.
Statistically Different
Being statistically different means that observed differences between groups or variables in a study are unlikely to have occurred by chance, according to statistical analysis. This distinction supports the idea that the observed effects reflect true differences in the populations being studied.
Q3: Exhibit 4-5.The following contingency table provides frequencies
Q9: We would like to determine the average
Q32: A valid reason for using a quantitative
Q54: A continuous variable assumes any value from
Q56: In its standard form,Chebyshev's theorem provides a
Q74: How do you define the range?<br>A)Q3 -
Q80: The total probability rule is useful only
Q83: Frequency distributions may be used to describe
Q83: When the required sample size calculated by
Q90: Mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events contain