Hervis Car Rental in Austin,Texas,has 50 high-performance Shelby-H Mustangs in its rental fleet.These cars will be in greater demand than usual during the last weekend in July when the Central Texas Mustang Club holds its annual rally in Austin.At times like this,Hervis uses a revenue management system to determine the optimal number of reservations to have available for the Shelby-H cars.Hervis has agreed to have at least 60% of its Shelby-H Mustangs available for rally attendees at a special rate.Although many of the rally attendees will request a Saturday and Sunday two-day package,some attendees may select a Saturday-only or a Sunday-only reservation.Customers not attending the rally may also request a Saturday and Sunday two-day package,or make a Saturday-only or Sunday-only reservation.Thus,six types of reservations are possible.The cost for each type of reservation is shown here. 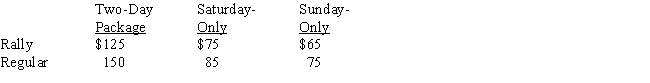 The anticipated demand for each type of reservation is as follows:
The anticipated demand for each type of reservation is as follows: 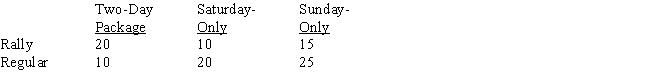 Hervis Car Rental would like to determine how many Shelby-H Mustangs to make available for each type of reservation in order to maximize total revenue.
Hervis Car Rental would like to determine how many Shelby-H Mustangs to make available for each type of reservation in order to maximize total revenue.
a.Define the decision variables.
b.Formulate a linear programming model for this revenue management application.
Definitions:
Targeted Customers
A specific group of consumers identified as the primary audience for a product or service, based on shared characteristics or needs.
Overall Strategy
A comprehensive plan detailing how a business or organization will achieve its goals and objectives.
Strategic Business Unit Level
A division or unit within a larger organization that operates with its own mission, vision, and objectives, and focuses on specific market segments.
Strategic Direction
The guidance provided by an organization to define its strategy and make decisions about allocating its resources to pursue this strategy.
Q5: A variation of the waiting line models
Q15: Financial planner Minnie Margin has a substantial
Q25: For many waiting line situations,the arrivals occur
Q27: Target values will never be met precisely
Q32: A valid reason for using a quantitative
Q41: Converting a transportation problem LP from cost
Q44: Simulation models that must take into account
Q49: A feasible solution is one that satisfies
Q51: Periodic review inventory systems<br>A)are less subject to
Q55: In the LP formulation of a maximal