The Hadfield Company manufactures and sells a unique electronic part. The company's plant is highly automated with low variable and high fixed manufacturing costs. Operating results on an absorption costing basis for the first three years of activity were as follows: 
Additional information about the company is as follows:
- Variable manufacturing costs (direct labor, direct materials, and variable manufacturing overhead) total $3 per unit, and fixed manufacturing overhead costs total $400,000.
- Fixed manufacturing costs are applied to units of product on the basis of the number of units produced each year (i.e., a new fixed manufacturing overhead rate is computed each year).
- The company uses a FIFO inventory flow assumption.
- Variable selling and administrative expenses are $2 per unit sold. Fixed selling and administrative expenses total $100,000.
- Production and sales information for the three years is as follows: 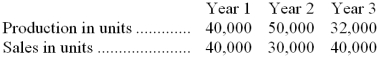
Required:
a. Compute net operating income for each year under the variable costing approach.
b. Referring to the absorption costing income statements above, explain why net operating income was higher in Year 2 than in Year 1 under absorption costing, in light of the fact that fewer units were sold in Year 2 than in Year 1.
c. Referring again to the absorption costing income statements, explain why the company suffered a loss in Year 3 but reported a profit in Year 1, although the same number of units was sold in each year.
d. If the company had used lean production during Year 2 and Year 3 and produced only what could be sold, what would the company's net operating income (loss) have been each year under absorption costing?
Definitions:
Complementary Goods
Products or services that are often used together because the consumption of one enhances the value or desire of the other.
Substitute Products
Goods or services that can be used in place of each other, satisfying essentially the same needs.
Ice Cream Sundaes
A dessert consisting of one or more scoops of ice cream topped with sauce or syrup, and often other toppings such as whipped cream, nuts, or cherries.
Successively Less Satisfaction
The phenomenon where each additional unit of a particular good or service consumed provides less satisfaction or utility than the previous one; also known as diminishing marginal utility.
Q3: To attain its desired ending cash balance
Q57: Yumm Dairy Corporation manufactures carrot-flavored ice cream.
Q62: If company A has a higher degree
Q66: Ben Company produces a single product. Last
Q96: The contribution margin for January was:<br>A) $172,000<br>B)
Q103: Since variable costing emphasizes costs by behavior,
Q103: The Tobler Company has budgeted production for
Q111: The selling and administrative expense budget of
Q180: The company's contribution margin ratio is closest
Q225: Garing Urban Diner is a charity supported