Wind chill is a combination of temperature and wind speed that expresses how cold the air feels. The larger the wind speed, the more rapidly heat is lost to the air and thus the colder it feels. The table shows the wind chill for selected temperatures and wind speeds. At 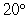 and a wind speed of 30 mph, how much change in wind chill can be expected if the wind speed increases by 10 mph? Temperature (degrees Fahrenheit)
and a wind speed of 30 mph, how much change in wind chill can be expected if the wind speed increases by 10 mph? Temperature (degrees Fahrenheit)
Wind speed
(mph) 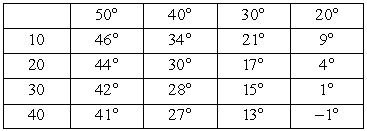
Definitions:
Incremental Manufacturing Cost
The additional costs incurred when manufacturing one additional unit of a product, essential for decision-making in production and pricing.
Units Produced
The total number of complete units that are manufactured during a specific period.
Indirect Manufacturing Cost
Costs related to production that cannot be directly attributed to specific products, such as maintenance, utilities, and supervision.
Units Produced
The total number of complete products that are manufactured or processed by a company within a specific period.
Q1: Identify the form of a particular solution
Q9: Identify the surface. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5869/.jpg" alt="Identify the
Q12: Given <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5869/.jpg" alt="Given ,
Q30: Find the absolute extrema of the function
Q49: The location <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5869/.jpg" alt="The location
Q59: Determine, by hand, the interval(s) where <img
Q63: Find the directions of maximum and minimum
Q68: Use a graphing utility to graph the
Q71: Using the position function <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5869/.jpg" alt="Using
Q97: Find an equation for the tangent plane