Early efforts to develop a vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) using inactivated virus were unsuccessful. Antibody responses to the vaccine were poor, and were not protective against the natural infection. Studies in mice revealed a likely explanation for the poor performance of the inactivated RSV vaccine. For these studies, inactivated RSV was generated by UV-treatment of the virus, and was referred to as UVRSV. This UVRSV was compared to live RSV in a number of assays. First, mice were immunized by footpad (intradermal, also known as subcutaneous) injection of either UVRSV or live RSV, and dendritic cells from the draining lymph node were isolated 24 hours later. Cell lysates from these dendritic cells were prepared, and were immunoblotted for the levels of I B protein, the inhibitory subunit of the cytosolic complex of NF B that is degraded following stimulation of receptors that activate NF B. A loading control of -actin is shown to indicate comparable amounts of total protein in each sample. 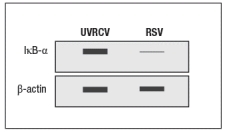
a) Given these data, name two classes of receptors in dendritic cells that might account for the difference seen in the immunoblot.
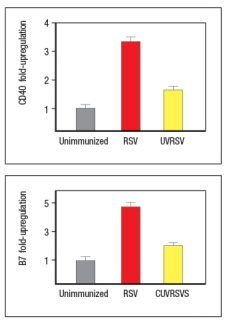
To examine further the different effects of the UVRSV versus live RSV immunization on dendritic cells, the dendritic cells were isolated from draining lymph nodes 24 hours after immunization and stained for surface expression of CD40 and the co-stimulatory B7 receptors. These data are shown in Figure as fold-increase over the levels of expression of these molecules detected on dendritic cells from unimmunized mice.
Next, mice were immunized with live RSV or UVRSV, and CD4 T cells were isolated from draining lymph nodes on various days post-immunization. The T cells were examined for IFN- production in response to viral antigens mixed with antigen-presenting-cells by ELISPOT, and the numbers of responding cells at each time point were graphed, as shown in Figure. 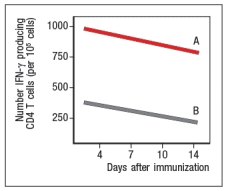
b) Which data (A or B) represents the live RSV versus the UVRSV, and why?
To determine which dendritic cell pathway might be important for the improved responses to live RSV compared to UVRSV, live RSV was used to immunize mice with reduced expression of the adapter protein, MyD88, and the responses of the Myd88+/- mice were compared to wild-type immunized mice. In these studies, anti-RSV antibodies in sera of immunized mice were tested for their ability to neutralize infectious virus in an in vitro assay, as shown in Figure. Log2PRNT indicates the amount the sera can be diluted before it loses the ability to neutralize 50% of the infectious virus in each sample, on a log2 scale (i.e., the higher the value the more potent the sera is for neutralizing virus).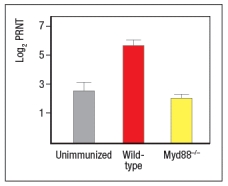
c) Based on these data, what is the likely identity of the receptor family required for live RSV immunization to produce neutralizing antibodies to RSV?
To determine whether the pathway identified above was responsible for the more robust response to live RSV compared to UVRSV, mice were immunized with UVRSV alone, UVRSV in combination with alum, or UVRSV in combination with synthetic double-stranded RNA (poly I:C) plus synthetic single-stranded RNA (poly U). The sera from these mice were then tested for their ability to neutralize infectious RSV, in comparison to sera from unimmunized mice or mice immunized with live RSV, as shown in . 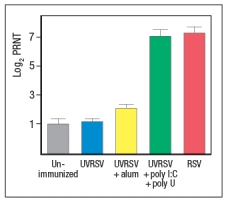
d) Do these data support or refute your answer to question (c) above? Do they implicate any specific receptors in the pathway required to generate a robust neutralizing antibody response to RSV?
Definitions:
Management Training
Programs aimed at enhancing the abilities of managers and potential managers to improve productivity and effectiveness in an organization.
Q6: The most common averse effects of anti-PD-1
Q8: Composed of a recombinant nonpathogenic virus carrying
Q11: All of the modular protein domains used
Q11: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\alpha"><span class="katex"><span class="katex-mathml"><math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><semantics><mrow><mi>α</mi></mrow><annotation encoding="application/x-tex">\alpha</annotation></semantics></math></span><span
Q16: Even when the complement cascade fails to
Q22: A mouse is immunized with the tetanus
Q27: Several pathogens produce proteins, either membrane-bound or
Q27: Both MHC class I and MHC class
Q31: At how many places does the curve
Q41: Human genome-wide genetic association (GWAS) studies have