Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common pathogen that nearly all children are infected with by age 2. It is currently the leading cause of hospitalization of infants. In 1966 a vaccine against RSV was developed and tested in children. The vaccine was made by inactivating RSV virions with formalin, and then injecting the inactivated virus into recipients; the vaccine was known as FIRSV . The top graph shows the results of an assay used to assess the relative affinities of antibodies in sera from immunized mice. Sera were isolated from mice immunized with live RSV versus FIRSV, and the isolated sera were tested for binding to immobilized RSV particles. The graph depicts the percentage of IgG antibody remaining bound to virus after washing in increasing concentrations of urea. The higher the affinity, the greater the amount of antibody that remains bound to antigen as the urea concentration increases. The bottom graph shows the titers of neutralizing antibody in the serum of mice immunized with FIRSV or with live RSV, compared to an unimmunized control. In this case, sera at different dilutions are mixed with live RSV, and then the mixture is tested for the amount of infectious virus remaining in solution. The log2 PRNT (50% plaque reduction) indicates the amount the serum can be diluted and still retain the ability to neutralize 50% of the virus particles. Based on these data, what is the likely explanation for the failure of the FIRSV vaccine to protect recipients? 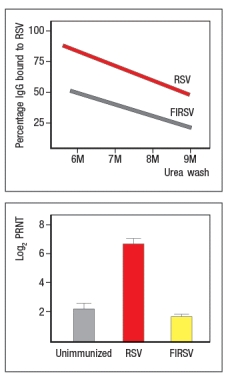
Definitions:
Expatriate
An individual who is temporarily or permanently residing in a country other than their native country, often for work reasons.
Overseas Service
Employment or deployment that occurs outside of an individual's home country, often implying work in foreign branches of multinational corporations or government posts.
Recognition
The act of acknowledging or giving official status to something or someone, often as a form of validation or appreciation.
Language Barriers
Obstacles to communication that occur due to differences in language between the communicating parties.
Q2: Mechanism of peripheral tolerance of B cells
Q4: Amino acid sequence analysis of all of
Q6: Inhibits macrophage cytokine secretion<br>A)Azathioprine<br>B)Cyclosporine<br>C)Mycophenolate mofetil<br>D)Rapamycin<br>E)Anti-CD40L antibody<br>F)Anti-IL-2R antibody<br>G)CTLA4-Ig<br>H)OKT3<br>I)Corticosteroids
Q8: Important in dendritic cell and T cell
Q10: Septic shock is a serious, often fatal
Q18: In humans, IgA is produced in copious
Q22: Evaluate the integral <span class="ql-formula"
Q36: Infants with RS-SCID generally require treatment by
Q74: Determine the number of real solutions
Q91: Find a parametric representation for the