Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a rather mild immunodeficiency disease that generally appears in young adults, with a peak onset between ages 20-30. Approximately 25% of the cases of CVID are familial, indicating a genetic basis for the disease. CVID patients suffer from recurrent infections of the respiratory tract, the ears, and the gastrointestinal tract. Common infections in these patients are caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. Analysis of their peripheral blood cells shows normal numbers and subsets of T cells. B cell data from peripheral blood are shown in Figure : 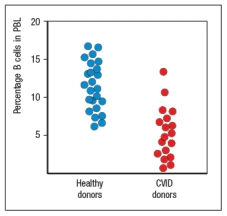
a) In general, what is the immune mechanism most likely defective in patients with CVID? Explain your reasoning.
One particular family is chosen for further study. In this family, two of four children have CVID, as shown in Figure 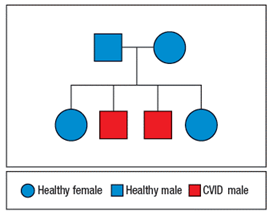
Given this pedigree, the mother’s peripheral blood leukocytes are examined for their patterns of X-chromosome inactivation. The results show that all of her T cells, B cells, and monocytes show random (50:50) inactivation of each of her X chromosomes.
b) What do these data indicate about the gene defect causing CVID in this family?
In a second series of studies, peripheral blood cells from one CVID patient and one healthy child in this family were collected, and T cell and B cell populations were separately isolated. These cell populations were mixed in different combinations, and then cultured for one week in the cytokines IL-4, IL-21, and IL-6. At the end of one week, the concentrations of secreted antibody in the culture supernatants were measured 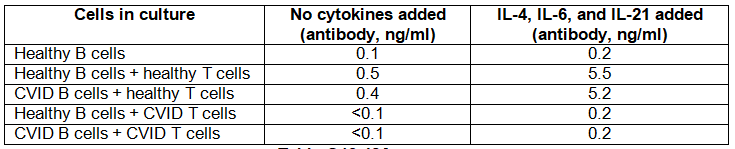
c) What do these data indicate about the gene defect causing CVID in this family?
In a final set of experiments, the isolated T cells and B cells from the study above were used in a transwell assay. In this assay, shown in Figure , cell populations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane. This allows soluble mediators to equilibrate between the top and bottom chambers, but prevents direct cell–cell contact.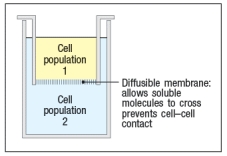
As a control, the cell populations were mixed together in the bottom chamber, a result that would replicate the findings from the study above. In addition, in this study, all wells contained IL-4, IL-6, and IL-21. After 7 days, culture supernatants were analyzed for antibody concentrations.The results of the transwell experiments are shown in Table .
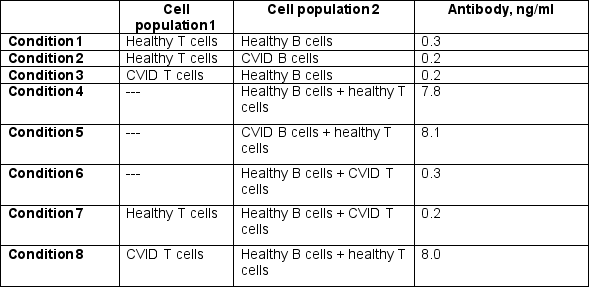
d) What do these data indicate about the function of the gene that is defective in the CVID patients from this family?
Definitions:
Manufacturing Business
A type of business that produces finished goods from raw materials by using various forms of machinery and human labor in a process known as manufacturing.
Factory Overhead
All the overhead costs related to the production process, except for the expenses on direct materials and direct labor.
Cost of Goods Sold
The direct costs attributed to the production of the goods sold by a company, including the cost of the materials and labor directly used to create the product.
Predetermined Overhead Rate
An estimated rate used to allocate manufacturing overhead costs to individual units of production.
Q3: The C3 convertase of the alternative complement
Q5: Which of the following infectious diseases was
Q5: A protein tyrosine kinase homologous to Zap-70,which
Q6: Eosinophils are a subset of granulocytes
Q8: Generated by factor I-mediated proteolysis,this complement fragment
Q11: Which of the following statements about the
Q13: Some CD1 molecules bind to glycosphingolipids,
Q14: NKG2D is an activating receptor expressed
Q32: In healthy adults, neutrophils represent approximately half
Q35: Unlike B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes do not