Synthesis question: Several vaccines against viral infections are made by isolating purified surface proteins of the viral particle, mixing them with an adjuvant to stimulate an innate immune response, and injecting the mixture into people. Two examples of this are the vaccine against Hepatitis B virus, and the vaccine against Human Papilloma Virus (the 'cervical cancer' vaccine). One interesting property of vaccines of this type (known as 'subunit vaccines') is that there is a requirement for a CD4 T cell response to the vaccine antigen in order to generate antibodies to the innocuous protein in the vaccine. In the case of the Hepatitis B vaccine, the viral protein included in the vaccine is the Hepatitis B surface antigen (HepB-SAg), a protein that is approximately 200 amino acids in length. The graph in Figure shows the data from immunizing individuals with this vaccine, and monitoring their production of protective antibody responses to the viral protein. 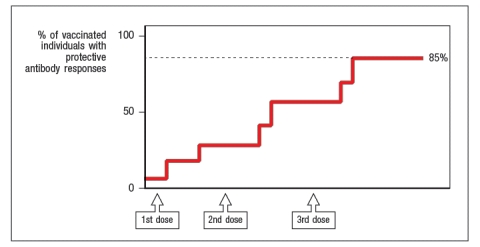
a) What results would be predicted if experiments were performed to examine the CD4 T cell responses to the HepB-SAg in these same individuals? In particular, indicate whether all individuals would show similar responses. Explain your reasoning.
b) Most vaccines, particularly those made by immunizing individuals with purified pathogen components, are designed to elicit robust antibody responses to the immunizing antigens. For vaccines against viral infections (like the HepB vaccine), the immune responses generated are only protective when administered prophylactically, i.e., before the individual is ever exposed to the pathogen. Why is it essential to vaccinate against viral infections before the individual is ever exposed to the virus?
Definitions:
Substitution Effect
That part of an increase (decrease) in amount consumed that is the result of a good being cheaper (more expensive) in relation to other goods because of a reduction (increase) in price.
Income Effect
The change in consumption resulting from a change in real income, typically due to a price change of goods or services.
Marginal Satisfaction
The change in satisfaction or utility that a consumer experiences from consuming an additional unit of a good or service.
Utility-Maximizing
The economic principle that consumers choose combinations of goods and services to maximize their satisfaction or utility under budget constraints.
Q5: Variable Ig domain<br>
Q8: Nonglycosylated red cell membrane protein missing or
Q11: All of the modular protein domains used
Q16: To avoid the potential for activating self-reactive
Q19: Six people have declared their intentions to
Q22: Our environment contains masses of microorganisms, many
Q27: The entry of naive T cells from
Q38: You have a decision to invest $10,000
Q42: Individuals with defects in T cell development
Q45: The Consumer Price Index (1982-84 = 100)