Infants and young children with deficiencies in specific complement components present with recurrent respiratory infections caused by extracellular bacteria. The peak age of susceptibility is between 6 and 12 months after birth. At this time, as shown in Figure , maternal antibodies acquired by the child during fetal gestation are nearly gone, but the child is not yet generating robust antibody responses to new infections, as indicated by the low circulating levels of IgG and IgA. As children with this immunodeficiency get older, they outgrow this disease and show no further evidence of these recurrent infections. Based on this information, name one likely gene deficiency (in the complement system) that could cause this primary immunodeficiency, and the specific complement pathway likely to be affected. Explain your answer. 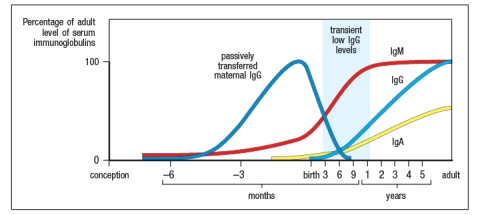
Definitions:
Activation-Synthesis
A theory suggesting that dreams are the brain's attempt to make sense of random neural activity that occurs during sleep, synthesizing this activity into coherent narratives.
Lateral Geniculate Nuclei
A pair of thalamic nuclei in the brain that act as primary relay centers for visual information received from the retina to the visual cortex.
The Elderly
A term used to describe individuals who are significantly above the typical age of retirement, often considered to be ages 65 and older.
Sleep
A naturally recurring state of mind and body characterized by altered consciousness, reduced sensory activity, inhibition of nearly all voluntary muscles, and decreased interactions with surroundings.
Q5: A survey of the opinions of property
Q9: Many of the inflammatory mediators produced by
Q19: The antibody protein has two functional domains,
Q22: Polymorphisms in the IL-2R <span class="ql-formula"
Q22: Dendritic cells in the skin, known as
Q24: Most effector T cells migrate out of
Q28: A recent strategy showing some promise for
Q32: Diacyl-glycerol (DAG) is one of the
Q92: i. For a goodness-of-fit test, the following
Q94: The following table classifies an individual in