Canadian Accounting classifies accounts receivable as "current", "late", and "not collectible". Industry figures show that 60% of A/R are current, 30% are late, and 10% are uncollectible. A law firm in Markham Ontario has 500 accounts receivable: 310 are current, 125 are late and 65 are not collectible. Are these numbers in agreement with the industry distribution? 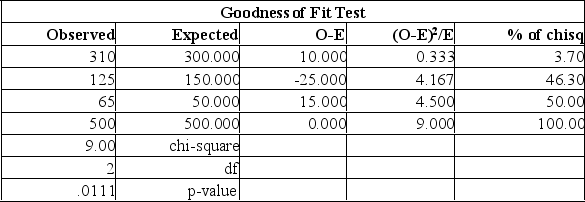 Using the data from this Mega stat printout, you determine:
Using the data from this Mega stat printout, you determine:
Definitions:
Marketplace
A physical or virtual space where goods and services are exchanged, typically involving multiple buyers and sellers.
Agricultural Societies
Communities whose economies are based primarily on the production and maintenance of crops and farmland, often signifying a shift from hunter-gatherer lifestyles.
Multipurpose Money
A concept in economics where money is used for various purposes beyond medium of exchange, including as a unit of account, a store of value, and a standard of deferred payment.
Merchant Capitalism
An economic phase in which merchants' wealth is accumulated through trade and the exploitation of international commerce, often preceding industrial capitalism.
Q3: An index which compares current prices times
Q7: i. The multiple standard error of estimate
Q14: An important transcription factor activated by
Q25: Figure shows the germ-line configuration of three
Q40: i. The irregular component of a time
Q42: The following data was collected comparing car
Q54: A student asked a statistics professor
Q68: A random sample of 30 executives from
Q94: The following table classifies an individual in
Q113: A sample of General Mills employees was