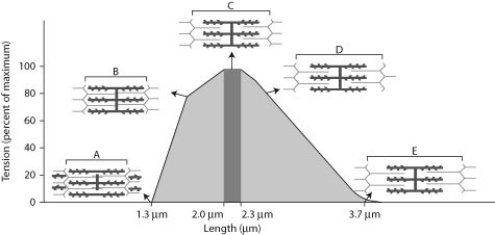
 When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension) . However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
When sarcomeres contract, they generate force (tension) . However, the amount of force generated depends on the sarcomere length and the amount of thick and thin filament overlap. Below is a figure that details the force-generating properties of a single sarcomere. This figure was modified from a scientific paper by Al Gordon and colleagues from 1966 and is a classic illustration of the relationship between sarcomere length and force.
-At what point on the graph is the sarcomere the most extended?
Definitions:
Expected Rate
The anticipated yield or return on an investment, loan, or other financial products over a specific period.
Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or variation in a set of values, indicating how much the values differ from the mean.
Risk-Free Asset
An investment with a guaranteed return and no chance of default, often used as a benchmark for the risk level of other investments.
Standard Deviation
A statistical measure that quantifies the amount of variability or dispersion of a set of data points or distribution from the mean.
Q8: The nervous system determines the pitch of
Q16: Suppose that scientists who study predator-prey relationships
Q19: Biologically, why might oxytocin have the nickname
Q25: The role of the nontreated males in
Q34: In a showy flower such as a
Q35: What is the role of the fungus
Q50: The two main classes of molecules that
Q51: The density of Douglas firs in an
Q54: You exercised to the point that you
Q59: A single PR protein is composed of