Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a common cause of sudden death and heart failure. Many mutations can cause DCM, but several of them are linked to the protein troponin, which is an essential protein that helps regulate muscle contraction in the heart.
-The A159E mutation causes an A amino acid to be replaced with an E amino acid (their structures are shown here) . What effects do you think the A159E mutation will have on the troponin protein? 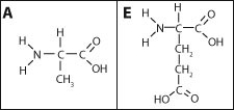
Definitions:
Media Personnel
Individuals involved in the creation, production, and dissemination of media content, such as journalists, editors, and broadcasters.
Agency
The capacity of individuals or groups to act independently and make their own free choices.
Counterbalancing
The method of compensating or neutralizing the effect of something by introducing a counteracting force or element.
Social Construction
The theory that many aspects of the world, including knowledge, are not inherently natural but are shaped by society's perceptions and actions.
Q2: Which group served as the control group
Q4: Which butterfly has changed gradually but significantly
Q6: You are studying a mini-ecosystem that you
Q7: In thinking about their role in cell
Q14: Miller-type experiments have shown that<br>A) simple cells
Q40: Which governmental body has the constitutionally delegated
Q47: Which of the following presidential powers have
Q55: The enzyme that converts information stored in
Q58: Microevolution, or evolution at its smallest scale,
Q69: Transduction<br>A) is the direct transfer of DNA