Mutant fruit flies that make only one antimicrobial peptide (defensin or drosomycin) were tested for survival after infection with Neurospora crassa fungi or with Micrococcus luteus bacteria, and the results are shown in Figures 35.1 and 35.2. 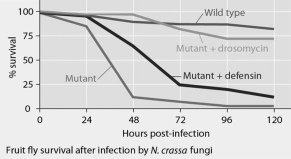
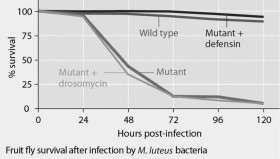
Figure 35.1 Figure 35.2
The results shown in the graphs in Figures 35.1 and 35.2 support the hypothesis that
Definitions:
Full Moon
The lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective, occurring when the Earth is located directly between the Sun and the Moon.
Random Sampling
A method of sampling that gives every member of a population an equal chance of being selected, ensuring the sample is representative of the entire population.
Blind Group Assignment
A method used in experiments where participants are randomly assigned to groups without knowing which group (e.g., experimental or control) they are in to reduce bias.
Random Group Assignment
A method used in experiments where participants are randomly assigned to different groups to ensure that each group has a similar composition at the start of the experiment.
Q9: Compared with the interstitial fluid that bathes
Q13: If you gently twist your earlobe, it
Q18: Which of the following hormones would be
Q19: In Figure 36.1, which numbers comprise the
Q22: Most land-dwelling invertebrates and all of the
Q34: There is a mutation in the gene
Q39: A nonfunctional CD4 protein on a helper
Q40: The presence of altruistic behavior is most
Q61: For a neuron with an initial membrane
Q71: An action potential can start in the