Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below, what is the standard cell potential for an electrochemical cell that has iron, Fe, and magnesium, Mg, electrodes? Also, identify the cathode. Standard Reduction
Potentials (volts) in Aqueous Solution 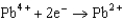 1.80
1.80 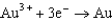 1.50
1.50 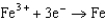 0.771
0.771 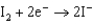 0.535
0.535 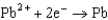 0.124
0.124 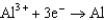 1.66
1.66 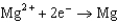 2.37
2.37 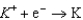 2.93
2.93
Definitions:
Percentage Of Completion
An accounting method used to recognize revenue and expenses of long-term contracts as a function of the estimated completion percentage of the project.
Direct Materials
Direct materials are the raw materials that are directly incorporated into a finished product and are a significant portion of the total production cost.
Equivalent Unit
A measure used in cost accounting to represent a portion of a product's costs when it is partially completed.
Finished Goods Inventory
The stock of completed products ready for sale at the end of an accounting period.
Q14: Starting with <font face="symbol"></font>G <font face="symbol"></font> <font
Q21: The standard entropy of diamond is 2.4
Q41: Because of recent advances in recovery technology,
Q54: What is the standard cell potential for
Q78: What other particle is formed in the
Q79: Three common weak bases are phosphate (P;
Q83: Which one of the following statements is
Q114: The unit of electrical power, watt (W),
Q143: When a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, the
Q149: The activity of a radioactive sample is