Given the following thermochemical equation detailing the combustion of glucose C6H12O6(s) 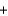 6O2(g)
6O2(g)  CO2(g)
CO2(g) 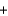 6H2O(g) Hrxn 2803 kJ/mol C6H12O6
6H2O(g) Hrxn 2803 kJ/mol C6H12O6
Determine the amount of glucose needed to release 30 kJ of energy.
Definitions:
Present Value
The immediate value of a prospective sum of money or succession of payments, with a certain rate of return.
Compound Interest
Compound interest refers to the interest that is computed on both the initial principal amount and the interest that has been accumulated from previous periods for either a deposit or a loan.
Future Value
The value of an investment or payment at a specific future date, considering factors like interest rates or earnings.
Present Value
The current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flow given a specified rate of return, often used in the assessment of investment profitability.
Q6: Most alkaline earth salts are soluble. Identify
Q16: Use the formal charge as a criterion
Q19: Which statements regarding combustion analysis to determine
Q25: Hartmann's solution is used in intravenous therapy
Q31: In one analysis, 1.34 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3835/.jpg" alt="In
Q98: Silicon is best described as a _<br>A)metalloid.<br>B)metal.<br>C)transition
Q110: What is the correct symbol for an
Q136: Copper was the first metal to be
Q141: _ is how gases spread among each
Q145: How many moles of propane are contained