Calcium hydride (CaH2) is so reactive with water that it can be used to remove traces of water from solvents other than water. If 24.6 g of calcium hydride is added to a large volume of solvent that contains 14.0 g of water, which of these remains, water or calcium hydride, after the reaction is complete? The reaction is: CaH2(s) 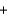 2H2O(l)
2H2O(l)  Ca(OH) 2(s)
Ca(OH) 2(s) 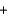 2H2(g)
2H2(g)
Definitions:
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
A common, opportunistic bacterium that can cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Antibiotic-Resistant
Refers to bacteria that have evolved the ability to survive exposure to antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Benign Bacteria
Non-pathogenic bacteria that do not cause disease and can be beneficial to their host organism.
Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Bacteria that have developed immunity to certain antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Q47: If 100 mL of 3.0 M solution
Q82: What is the correct name for Ni(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>?<br>A)nickel
Q101: He is the symbol for _<br>A)hydrogen.<br>B)hafnium.<br>C)mercury.<br>D)helium.<br>E)holmium.
Q102: Given the standard enthalpies of formation for
Q107: You hold a 50 g sphere of
Q116: Sketch the graph of the polar equation.
Q117: Which of the following phosphate compounds is
Q124: How many nitrogen atoms are there in
Q130: Use the following information to determine the
Q163: What is the average kinetic energy (in