Exhibit 3.3
The following questions are based on this problem and accompanying Excel windows.
Jack's distillery blends scotches for local bars and saloons. One of his customers has requested a special blend of scotch targeted as a bar scotch. The customer wants the blend to involve two scotch products, call them A and B. Product A is a higher quality scotch while product B is a cheaper brand. The customer wants to make the claim the blend is closer to high quality than the alternative. The customer wants 50 1500 ml bottles of the blend. Each bottle must contain at least 48% of Product A and at least 500 ml of B. The customer also specified that the blend have an alcohol content of at least 85%. Product A contains 95% alcohol while product B contains 78%. The blend is sold for $12.50 per bottle. Product A costs $7 per liter and product B costs $3 per liter. The company wants to determine the blend that will meet the customer's requirements and maximize profit. 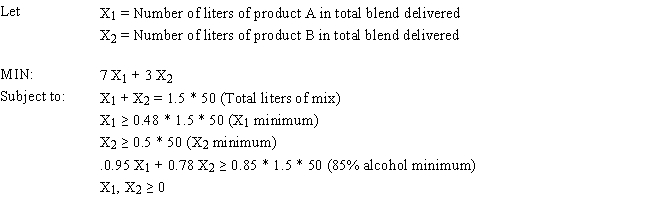
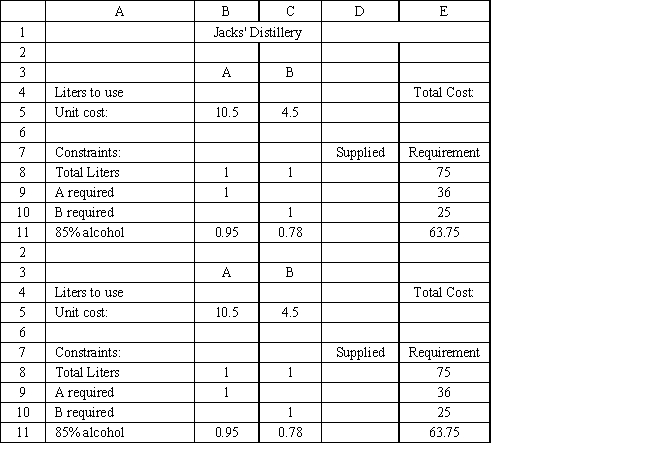
-Refer to Exhibit 3.3. Which cells should be the constraint cells in this problem?
Definitions:
Relative Frequency Histogram
A type of histogram that displays the relative frequencies, or proportions, of data points within specified intervals.
Open-ended Classes
A teaching or learning style with no predetermined limits on the topics to be explored or the depth of inquiry.
Equal Width Classes
A method in data binning where each class or bin has the same width, used in the construction of histograms and frequency distributions.
Mutually Exclusive Classes
Categories or groups that cannot occur simultaneously, implying that the occurrence of one event precludes the occurrence of another.
Q2: Refer to the above production possibilities curves.
Q6: Refer to Exhibit 3.2. What formula should
Q10: A company wants to locate a new
Q22: Solve the following LP problem graphically by
Q37: Refer to Exhibit 7.4. Given the solution
Q37: Refer to Exhibit 6.1. What values would
Q69: The production possibilities curve tells us:<br>A) what
Q72: Find the maximum solution on this graph
Q83: A problem in which some decision variables
Q219: Opportunity cost is best defined as:<br>A) the