Exhibit 10.1
The following questions are based on the problem description and the output below.
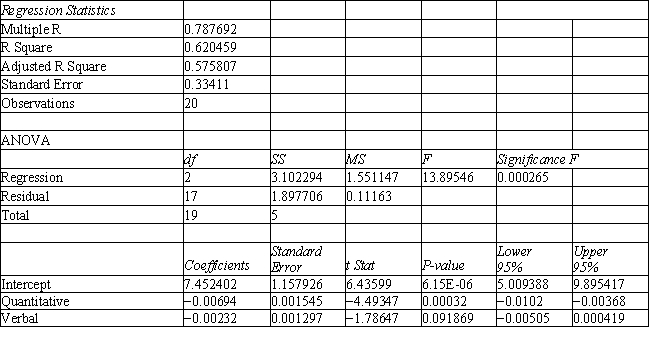
A college admissions officer wants to evaluate graduate school applicants based on their GMAT scores, verbal and quantitative. Students are classified as either successful or not-successful in their graduate studies. The officer has data on 20 current students, ten of whom are doing very well (Group 1) and ten who are not (Group 2) . 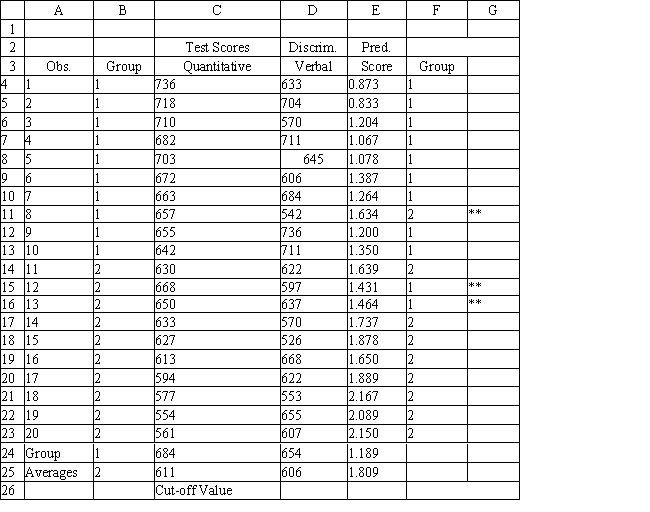

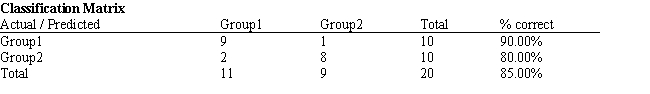
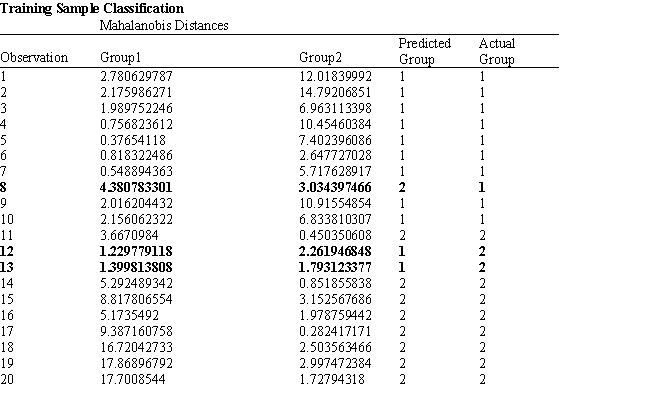
-Refer to Exhibit 10.1. Suppose that for a given observation, the difference between Mahalanobis distances between group 1 and 2 (G1-G2) is small. This means that
Definitions:
Consolidation Theory
A theory suggesting that memories become more stable in the brain over time, moving from short-term to long-term storage through a process of consolidation.
Traumatic Brain Injury
Damage to the brain caused by an external mechanical force, potentially leading to long-term complications or death.
Sleep Deprivation
A condition resulting from not getting enough sleep, which can affect cognitive functions, physical health, and emotional well-being.
Consolidation
the process by which memories become stable in the brain, transforming from a short-term to a long-lasting form.
Q8: Joe's Copy Center has 10 copiers. They
Q12: Leaves of a decision tree are also
Q14: An office supply company is attempting to
Q33: When using the Regression tool in Excel
Q49: The terms b<sub>0</sub> and b<sub>1</sub> are referred
Q54: The M in M/G/1 stands for<br>A) Markovian
Q70: The second step in Goal Programming is
Q76: Using the information in Exhibit 12.3, what
Q76: A Gantt chart is a popular technique
Q94: Which are characteristics of decision-making under uncertainty?<br>A)