The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
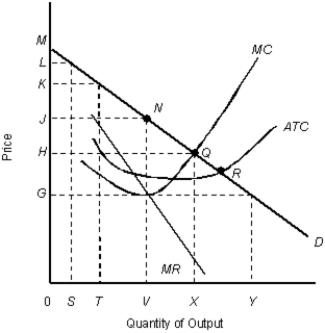 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-If a firm is able to collect the entire producer surplus, it is said to have practiced perfect price discrimination.
Definitions:
Interact
To act in such a manner as to have an effect on another; in biology, it often refers to the way biological entities, such as molecules or organisms, affect each other.
Interdependent
The reciprocal relationship between entities where each depends on the other, leading to a situation where their interactions significantly influence their viability or functionality.
Systems Biology
A field of biology that synthesizes knowledge of many small parts to understand the whole. Also referred to as integrative biology or integrative systems biology.
Integrative Biology
A field of biology that focuses on the integration of diverse scientific disciplines to understand biological complexity at various levels, from molecules to ecosystems.
Q10: The available credit limit we have in
Q12: If a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm is
Q22: In the short run, a monopolistically competitive
Q42: Firms under perfect competition produce:<br>A)homogeneous products.<br>B)unique products.<br>C)either
Q55: By discriminating between the consumers, the monopolist
Q64: When the perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
Q64: Other things equal, an increase in the
Q71: Investment is considered to be positively correlated
Q87: The table given below reports the value
Q87: For a perfectly competitive firm the break-even