Two probes, A and B, hybridize very near each other in a region of DNA that contains RFLPs when digested with HindIII. The four maps show the location and intervening distances of the HindIII restriction sites and the binding locations of probes A and B. The maps show alleles H1-H4 present in a population. What band(s) is/are seen in Southern blot analysis of a H2H3 heterozygote using probe B? 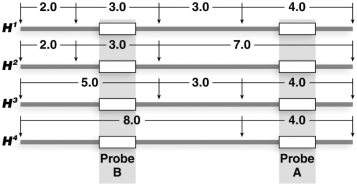
Definitions:
Melting Point
The point at which a solid transitions into a liquid under the conditions of atmospheric pressure.
Brønsted-Lowry
A theory in chemistry that defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
Organic Molecules
Chemical compounds containing carbon atoms bonded together and with other elements, typically forming the basis of life on Earth.
Q7: From a standpoint of natural selection, we
Q10: Transcomplementation is a name sometimes given for
Q17: If you wish to target a retrovirus
Q18: The allele responsible for the Siamese coat-color
Q20: Describe the hypothesis that James Neel proposed
Q26: Which enzyme is the product of the
Q32: If a gene in Drosophila is expressed
Q39: During translation initiation in prokaryotes, the amino
Q43: What are the two categories of gain-of-function
Q49: DNA glycosylase inhibitors are used to study