A recently discovered bacterium carries out ATP synthesis coupled to the flow of electrons through a chain of carriers to some electron acceptor. The components of its electron transfer chain differ from those found in mitochondria; they are listed below with their standard reduction potentials. 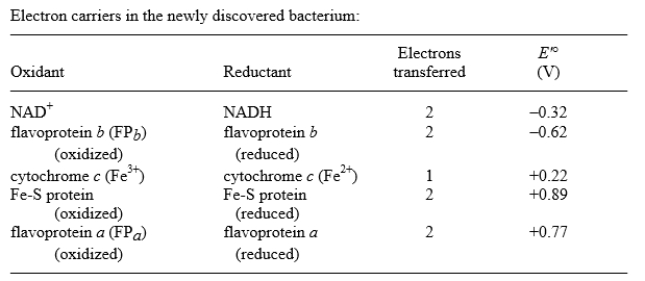 (a) Place the electron carriers in the order in which they are most likely to act in carrying electrons. (b) Is it likely that O2 (for which E'° = 0.82 V) is the final electron acceptor in this organism? Why or why not? (c) How would you calculate the maximum number of ATP molecules that could theoretically be synthesized, under standard conditions, per pair of electrons transfered through this chain of carriers? (The Faraday constant,
(a) Place the electron carriers in the order in which they are most likely to act in carrying electrons. (b) Is it likely that O2 (for which E'° = 0.82 V) is the final electron acceptor in this organism? Why or why not? (c) How would you calculate the maximum number of ATP molecules that could theoretically be synthesized, under standard conditions, per pair of electrons transfered through this chain of carriers? (The Faraday constant, 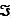 , is 96.48 kJ/V · mol.) G'° for ATP synthesis is +30.5 kJ/mol.
, is 96.48 kJ/V · mol.) G'° for ATP synthesis is +30.5 kJ/mol.
Definitions:
Null Hypothesis
A statement used in statistics that proposes there is no significant difference or effect in a given set of observations.
Directional
Pertaining to or indicating the direction in which something is oriented or moves.
Alternative Hypothesis
The hypothesis that proposes a specific relationship between variables, tested against the null hypothesis in statistical analysis.
Alternative Hypothesis
In statistical testing, the hypothesis that suggests there is a significant difference between the specified populations, contrary to the null hypothesis.
Q12: In an anaerobic muscle preparation, lactate formed
Q13: Which type of reaction is found in
Q14: Which diagram CORRECTLY represent a hydrogen bond?
Q32: Metabolic pathways are said to operate in
Q61: Which statement is NOT true of electron
Q75: The standard reduction potential for ubiquinone
Q83: Precursors for the biosynthesis of the pyrimidine
Q88: Diagram the path of electron flow from
Q99: Which intermediate of the citric acid cycle
Q104: In mammals, what process does NOT