A financial analyst examines the performance of two mutual funds and claims that the variances of the annual returns for the bond funds differ.To support his claim,he collects data on the annual returns (in percent) for the years 2001 through 2010.The analyst assumes that the annual returns for the two emerging market bond funds are normally distributed.Use the following summary statistics. 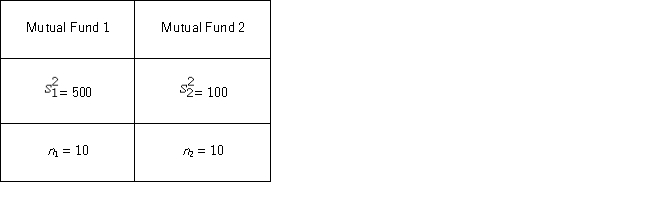 For the competing hypotheses
For the competing hypotheses 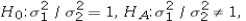 which of the following is the correct approximation of the p-value?
which of the following is the correct approximation of the p-value?
Definitions:
Fixed Costs
Expenses that do not change with the level of output or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance.
Diseconomies of Scale
The phenomenon where production cost per unit increases as the scale of output increases, usually due to factors like increased complexity and inefficiencies.
Long-run Average Total Cost
The per unit cost of production when all inputs, including capital, are variable, typically depicting economies and diseconomies of scale.
Marginal Cost
The additional cost resulting from the creation of one more unit of a product or service.
Q6: In the estimation of a multiple regression
Q10: An marketing analyst wants to examine the
Q26: A university has six colleges and takes
Q69: Many cities around the United States are
Q77: The following frequency distribution shows the monthly
Q84: A newly hired basketball coach promised a
Q84: In the following table,likely voters' preferences of
Q88: For a given confidence level and sample
Q108: The ages of MBA students at a
Q120: A researcher analyzes the factors that may