The textbook shows that ln(x + Δx)- ln(x)≅ 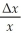 .Show that this is equivalent to the following approximation ln(1 + y)≅ y if y is small.You use this idea to estimate a demand for money function,which is of the form m = β0 ×
.Show that this is equivalent to the following approximation ln(1 + y)≅ y if y is small.You use this idea to estimate a demand for money function,which is of the form m = β0 × 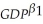 ×,
×, 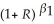 × eu where m is the quantity of (real)money,GDP is the value of (real)Gross Domestic Product,and R is the nominal interest rate.You collect the quarterly data from the Federal Reserve Bank of St.Louis data bank ("FRED"),which lists the money supply and GDP in billions of dollars,prices as an index,and nominal interest rates in percentage points per year
× eu where m is the quantity of (real)money,GDP is the value of (real)Gross Domestic Product,and R is the nominal interest rate.You collect the quarterly data from the Federal Reserve Bank of St.Louis data bank ("FRED"),which lists the money supply and GDP in billions of dollars,prices as an index,and nominal interest rates in percentage points per year
You generate the variables in your regression program as follows: m = (money supply)/price index;GDP = (Gross Domestic Product/Price Index),and R = nominal interest rate in percentage points per annum.Next you perform the log-transformations on the real money supply,real GDP,and on (1+R).Can you for see a problem in using this transformation?
Definitions:
Diagnose Situation
The process of analyzing and understanding a situation to identify the nature of a problem, challenge, or opportunity.
Disequilibrium
In economics, a state where market supply and demand are not balanced, leading to inconsistency in prices and quantities.
Unfreezing
The initial phase in the change process where existing patterns or behaviors are challenged to facilitate transition.
Organizational Politics
Activities within an organization aimed at improving individual or group positions and interests, often at the expense of others.
Q6: You have collected data on individuals and
Q10: Your textbook uses the following example of
Q18: (Continuation from Chapter 4,number 6)The neoclassical growth
Q19: Enterprise risk management is a process in
Q21: Which of the following instruments could be
Q31: A credit default swap is an ordinary
Q36: Which of the following techniques is a
Q40: Consider the following population regression function: Y
Q44: You try to explain the number of
Q48: To prove that the OLS estimator is