The Solow growth model suggests that countries with identical saving rates and population growth rates should converge to the same per capita income level.This result has been extended to include investment in human capital (education)as well as investment in physical capital.This hypothesis is referred to as the "conditional convergence hypothesis," since the convergence is dependent on countries obtaining the same values in the driving variables.To test the hypothesis,you collect data from the Penn World Tables on the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker (g6090)for the 1960-1990 sample period,and regress it on the (i)initial starting level of GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960 (RelProd60), (ii)average population growth rate of the country (n), (iii)average investment share of GDP from 1960 to 1990 (SK - remember investment equals savings),and (iv)educational attainment in years for 1985 (Educ).The results for close to 100 countries is as follows: 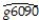 = 0.004 - 0.172 × n + 0.133 × SK + 0.002 × Educ - 0.044 × RelProd60,
= 0.004 - 0.172 × n + 0.133 × SK + 0.002 × Educ - 0.044 × RelProd60, 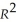 =0.537,SER = 0.011
=0.537,SER = 0.011
(a)Interpret the results.Do the coefficients have the expected signs? Why does a negative coefficient on the initial level of per capita income indicate conditional convergence ("beta-convergence")?
(b)Equations of the above type have been labeled "determinants of growth" equations in the literature.You recall from your intermediate macroeconomics course that growth in the Solow growth model is determined by technological progress.Yet the above equation does not contain technological progress.Is that inconsistent?
Definitions:
Market Failure
A situation where the allocation of goods and services by a free market is not efficient, often leading to negative externalities or a lack of public goods.
Competitive Market
A market structure characterized by a large number of buyers and sellers, free entry and exit, and a product for which each seller offers an identical product.
Deadweight Loss
A loss in economic efficiency that occurs when equilibrium for a good or service is not achieved or is not achievable.
Price Floor
A government-imposed limit on how low a price can be charged for a product, service, or commodity.
Q3: An estimator is<br>A)an estimate.<br>B)a formula that gives
Q11: Volatility clustering<br>A)is evident in most cross-sections.<br>B)implies that
Q19: The mean and variance of a Bernoille
Q22: The assumption that X has full column
Q31: Currency swap volume is greater than equity
Q31: A standard (Black-Scholes)European option is equivalent to
Q37: Which of the following is not a
Q44: A contingent-pay option allows the holder to
Q55: If the target beta exceeds the underlying's
Q61: The following types of statistical inference are