(Continuation of the Purchasing Power Parity question from Chapter 4)The news-magazine The Economist regularly publishes data on the so called Big Mac index and exchange rates between countries.The data for 30 countries from the April 29,2000 issue is listed below:
Price of Actual Exchange Rate
Country Currency Big Mac per U.S.dollar
Indonesia Rupiah 14,500 7,945
Italy Lira 4,500 2,088
South Korea Won 3,000 1,108
Chile Peso 1,260 514
Spain Peseta 375 179
Hungary Forint 339 279
Japan Yen 294 106
Taiwan Dollar 70 30.6
Thailand Baht 55 38.0
Czech Rep.Crown 54.37 39.1
Russia Ruble 39.50 28.5
Denmark Crown 24.75 8.04
Sweden Crown 24.0 8.84
Mexico Peso 20.9 9.41
France Franc 18.5 7.07
Israel Shekel 14.5 4.05
China Yuan 9.90 8.28
South Africa Rand 9.0 6.72
Switzerland Franc 5.90 1.70
Poland Zloty 5.50 4.30
Germany Mark 4.99 2.11
Malaysia Dollar 4.52 3.80
New Zealand Dollar 3.40 2.01
Singapore Dollar 3.20 1.70
Brazil Real 2.95 1.79
Canada Dollar 2.85 1.47
Australia Dollar 2.59 1.68
Argentina Peso 2.50 1.00
Britain Pound 1.90 0.63
United States Dollar 2.51
The concept of purchasing power parity or PPP ("the idea that similar foreign and domestic goods … should have the same price in terms of the same currency," Abel,A.and B.Bernanke,Macroeconomics,4th edition,Boston: Addison Wesley,476)suggests that the ratio of the Big Mac priced in the local currency to the U.S.dollar price should equal the exchange rate between the two countries.
After entering the data into your spread sheet program,you calculate the predicted exchange rate per U.S.dollar by dividing the price of a Big Mac in local currency by the U.S.price of a Big Mac ($2.51).To test for PPP,you regress the actual exchange rate on the predicted exchange rate.
The estimated regression is as follows: 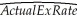 = -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994,n = 29,SER = 122.15
= -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994,n = 29,SER = 122.15
(23.74)(0.02)
(a)Your spreadsheet program does not allow you to calculate heteroskedasticity robust standard errors.Instead,the numbers in parenthesis are homoskedasticity only standard errors.State the two null hypothesis under which PPP holds.Should you use a one-tailed or two-tailed alternative hypothesis?
(b)Calculate the two t-statistics.
(c)Using a 5% significance level,what is your decision regarding the null hypothesis given the two t-statistics? What critical values did you use? Are you concerned with the fact that you are testing the two hypothesis sequentially when they are supposed to hold simultaneously?
(d)What assumptions had to be made for you to use Student's t-distribution?
Definitions:
Institutions
Structures or mechanisms of social order governing the behavior of a set of individuals within a given community, including laws, norms, and organizations.
Productive
The quality of being able to produce a substantial amount of goods, services, or crops efficiently and effectively.
Self-Disciplined
The ability to control one’s feelings, impulses, and actions, and to pursue goals with perseverance and determination.
Middle-Class Culture
Describes the values, norms, and practices of the middle class, often associated with economic stability, education, and manners.
Q2: In the case of heterogeneous causal effects,the
Q11: In the model ln(Yi)= β0 + β1Xi
Q20: Autoregressive distributed lag models include<br>A)current and lagged
Q22: The Solow growth model suggests that countries
Q22: A peer of yours,who is a major
Q34: A short hedger wants the basis to
Q35: The Times Series Regression with Multiple Predictors<br>A)is
Q42: Sample selection bias occurs when<br>A)the choice between
Q57: (Requires Calculus)For the case of the multiple
Q63: Use the definition for the conditional distribution