Let 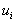 be distributed N(0,
be distributed N(0, 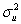 ),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in
),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in 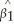 being distributed N(β1,
being distributed N(β1, 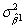 ),where
),where 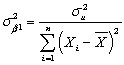 .Statistical inference would be straightforward if
.Statistical inference would be straightforward if 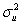 was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace
was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace 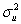 with an estimator
with an estimator 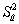 .Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect
.Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect 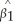 to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about
to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about 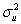 can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
Definitions:
Follicular Phase
The stage of a woman's menstrual cycle during which follicles in the ovary mature, ending with ovulation.
Placenta
An organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy, providing oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby while removing waste products from the baby's blood.
IUD
An intrauterine device, a small contraceptive device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Birth Control
Methods, devices, or medications used to prevent pregnancy, allowing individuals or couples to determine the timing and spacing of childbirth.
Q8: You have collected quarterly data on Canadian
Q21: Suppose that you have just read a
Q27: In the multiple regression model,the adjusted R2,
Q29: The value of a pay-fixed,receive-floating interest rate
Q32: A type I error is<br>A)always the same
Q39: Finding a small value of the p-value
Q42: Your textbook used a distributed lag model
Q42: The difference between the central limit theorems
Q48: Imagine that you were told that the
Q61: (Requires Statistics background beyond Chapters 2 and