In a simple regression with an intercept and a single explanatory variable,the variation in Y 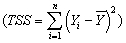 can be decomposed into the explained sums of squares
can be decomposed into the explained sums of squares 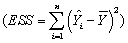 and the sum of squared residuals
and the sum of squared residuals 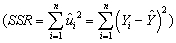 (see,for example,equation (4.35)in the textbook).
(see,for example,equation (4.35)in the textbook).
Consider any regression line,positively or negatively sloped in {X,Y} space.Draw a horizontal line where,hypothetically,you consider the sample mean of Y 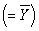 to be.Next add a single actual observation of Y.
to be.Next add a single actual observation of Y.
In this graph,indicate where you find the following distances: the
(i)residual
(ii)actual minus the mean of Y
(iii)fitted value minus the mean of Y
Definitions:
Elimination
The process of removing something or someone from consideration, or the body's process of expelling waste.
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections, toxins, medications, or autoimmune disease.
Hepatoma
A malignant tumor of the liver, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma, which is common in individuals with chronic liver diseases.
Nephritis
Inflammation of the kidneys, which can alter their function and is classified by the location such as glomerulonephritis or interstitial nephritis.
Q15: The two conditions for a valid instrument
Q16: One of the central predictions of neo-classical
Q16: Consider the AR(1)model Yt = β0 +
Q21: If you wanted to test,using a 5%
Q23: What would the correlation coefficient be if
Q30: The figure shows is a plot and
Q46: Time series variables fail to be stationary
Q46: "I am an applied econometrician and therefore
Q48: The mean of the sample average <img
Q52: In the regression model Yi = β0